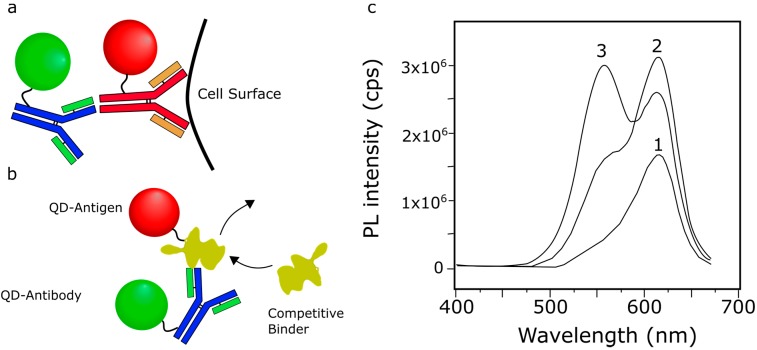
Figure 12.
(a) Schematic for sensing primary-secondary antibody interaction. Binding of the QD-labeled secondary antibody to the QD-labeled primary antibody brings the donor and acceptor QDs into close proximity, inducing FRET; (b) Schematic of competative antibody-antigen binding assay. The QD-labeled antibody binds to a QD-labeled antigen, bringing the donor and acceptor QDs into close enough proximity for efficient energy transfer. In the presence of additional antigen (e.g., an unlabeled endogenous molecule), the QD-labeled antigen is displaced, reducing energy transfer and yielding a measurable change in the PL of the system. Using an unlabeled antigen as the competitive binder reveals the antigen-antibody binding affinity. Schematics are not drawn to scale; (c) PL spectra demonstrating that competitive binding can reverse FRET signal. (c1) PL spectrum of QD-antibody (acceptors only); (c2) PL spectrum of QD-antigen bound to QD-antibodies, showing increased acceptor intensity due to FRET; (c3) PL spectrum of the QD-antigen + QD-antibody complex in the presence of the competitive binder, showing an increase in the donor peak intensity and decrease in the acceptor peak intensity; (c) Reprinted with permission from [88]. Copyright (2002) American Chemical Society.