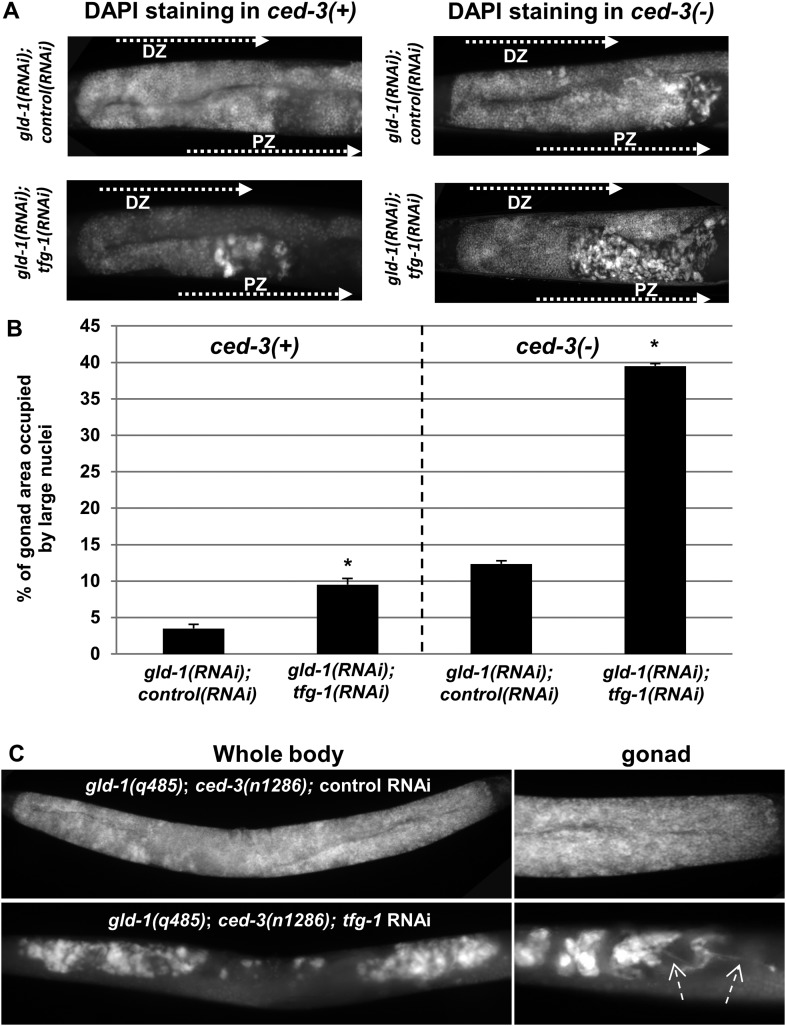
Figure 2. Ectopic cells with large nuclei accumulate in the gonads of gld-1; ced-3 animals.
(A) Representative micrographs (x400) of DAPI-stained gonads of day-4 animals. Animals were treated with the indicated RNAi. gld-1 RNAi was used to induce a germline tumor. ced-3 RNAi served to block apoptosis. tfg-1 RNAi was used to induce ER stress. Treatment with tfg-1 RNAi increased the levels of ectopic cells with large misshaped nuclei at the proximal zone of the gonad of gld-1 deficient animals, especially upon apoptosis inactivation. DZ marks the distal zone of the gonad. PZ marks the proximal zone of gonad. (B) Bar graph presents percentage of gonad area occupied by large nuclei in the indicated genotypes (n = at least 60 gonads per genotype). Asterisks mark Student's T-test values of p < 0.001 of tfg-1 RNAi-treated animals compared to their non-stressed controls. Note that ectopic cells with large nuclei were detected to different extents in most of the animals examined (see Figure 2—figure supplement 1). (C) The induction of ectopic cells in the gonad by tfg-1-induced ER stress was recapitulated in gld-1(q485); ced-3(n1286) double mutants. Arrows point at axon-like structures detected within the gonads of gld-1-deficient animals upon ER stress.