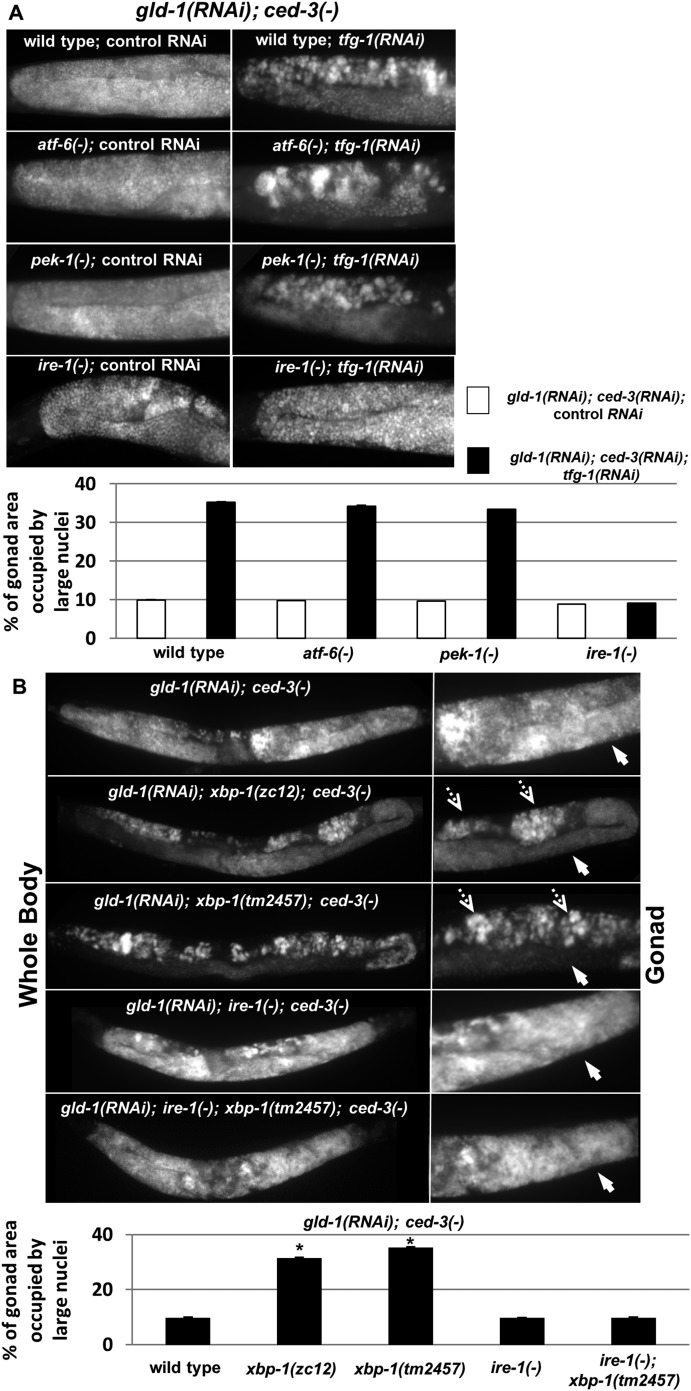
Figure 4. ER stress induces germline transdifferentiation in an ire-1-dependent but xbp-1-independent manner.
(A) Representative micrographs (x400) of DAPI-stained gonads of day-4 animals treated with either a mixture of control, gld-1and ced-3 RNAi or with a mixture of tfg-1, gld-1and ced-3 RNAi. Treatment with tfg-1, gld-1and ced-3 RNAi failed to induce germ cell transdifferentiation in ire-1 mutants. (B) Representative micrographs of whole body (x100) and gonads (x400) of DAPI-stained day-4 animals of the indicated genotypes treated with gld-1 and ced-3 RNAi. Solid arrows indicate mitotic germ cells. Dashed arrows indicate somatic nuclei. Bar graphs present percentage of gonad area occupied by ectopic cells. Asterisk marks Student's T-test of p < 0.001 relative to wild-type animals. Bar graphs present percentage of gonad area occupied by ectopic cells of the indicated genotypes (n = at least 70 gonads per genotype). Asterisks mark Student's T-test of p < 0.001 relative to the same animals treated with control, gld-1and ced-3 RNAi. Note that both alleles of xbp-1 similarly increased the percentage of gonad area occupied by ectopic somatic cells (p = 0.23).