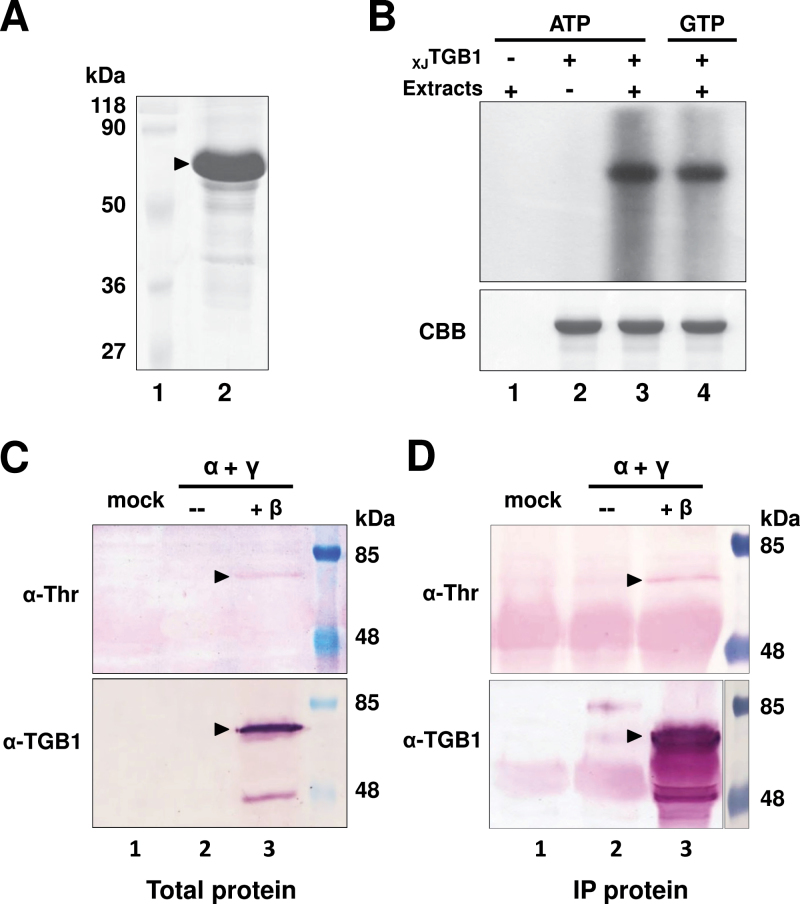
Fig. 2.
Phosphorylation of the XJTGB1 protein in vitro and in vivo. (A) Coomasie Brilliant Blue (CBB) staining of recombinant XJTGB1 protein purified from E. coli cells. Molecular weight markers (Fermentas) are indicated on the left side of the gel. (B) In vitro phosphorylation of purified XJTGB1 protein by cellular kinases present in healthy N. benthamiana extracts in the absence or presence of [γ-32P]ATP or [γ-32P]GTP. After the phosphorylation reactions, the TGB1 proteins were separated by 12.5% SDS-PAGE and the incorporated radioactivity was analysed by autoradiography. Reaction mixtures lacking XJTGB1 protein or N. benthamiana protein extracts served as negative controls. The CBB staining in the lower panel indicates that similar amounts of the XJTGB1 protein were present in each in vitro phosphorylation reaction. (C) In vivo phosphorylation of XJTGB1 protein in N. benthamiana by Western blotting with α-TGB1 polyclonal antibodies and α-threonine antibodies. A mock agroinfiltration lacking XJRNAβ was used as a negative control and molecular weight markers (Thermo Scientific) were used to estimate the size of the XJTGB1 protein. (D) In vivo phosphorylation of XJTGB1 protein immunoprecipitated (IP) from N. benthamiana was analysed as in Fig. 2C. (This figure is available in colour at JXB online.)