Fig 4. Neural Connectomics Puzzling Overview.
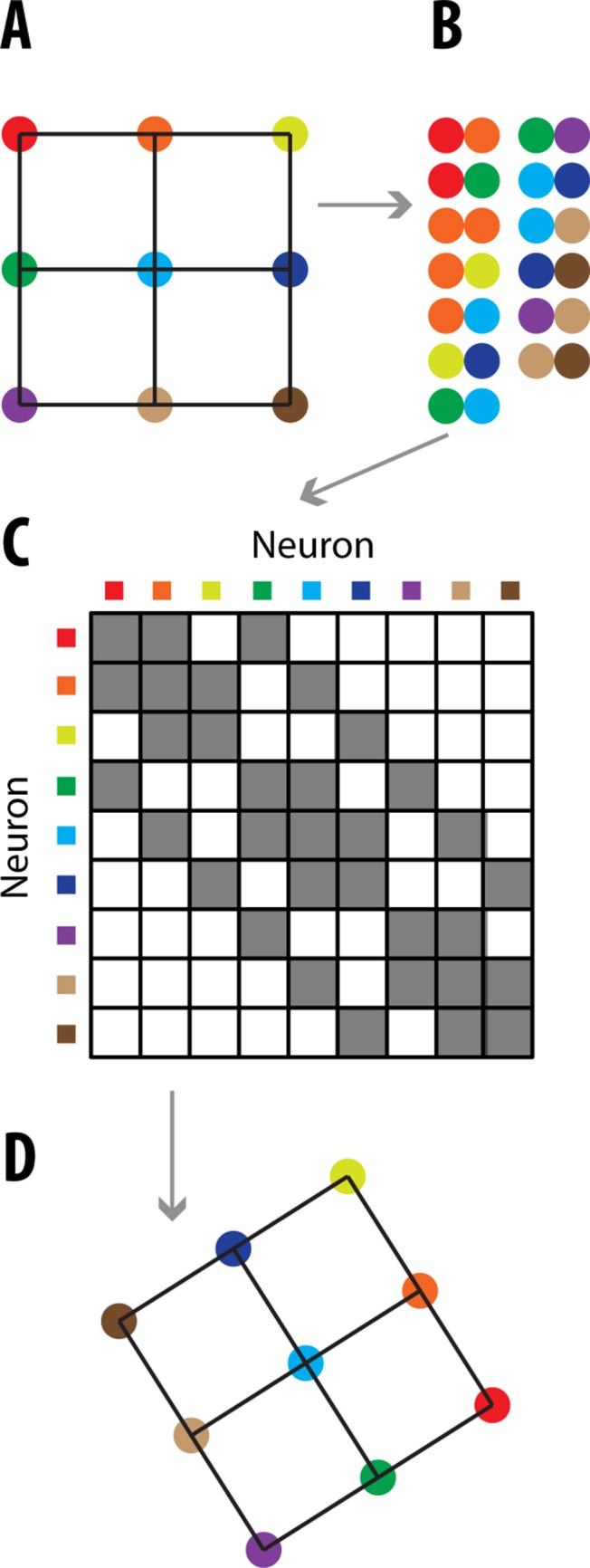
(A) An example of 9 connected neurons (circles). Lines signify connections. (B) After the brain is homogenized, the only remaining information is a record of the connections. Connections are shown here as adjacent circles. (C) A connectivity matrix is constructed describing the connections between neurons. Gray signifies a connection. Since connections are correlated with how close neurons are to one another, this connectivity matrix can be treated as the similarity matrix. (D) The neurons are puzzled back together. The formation may be rotated or flipped, as shown here.
