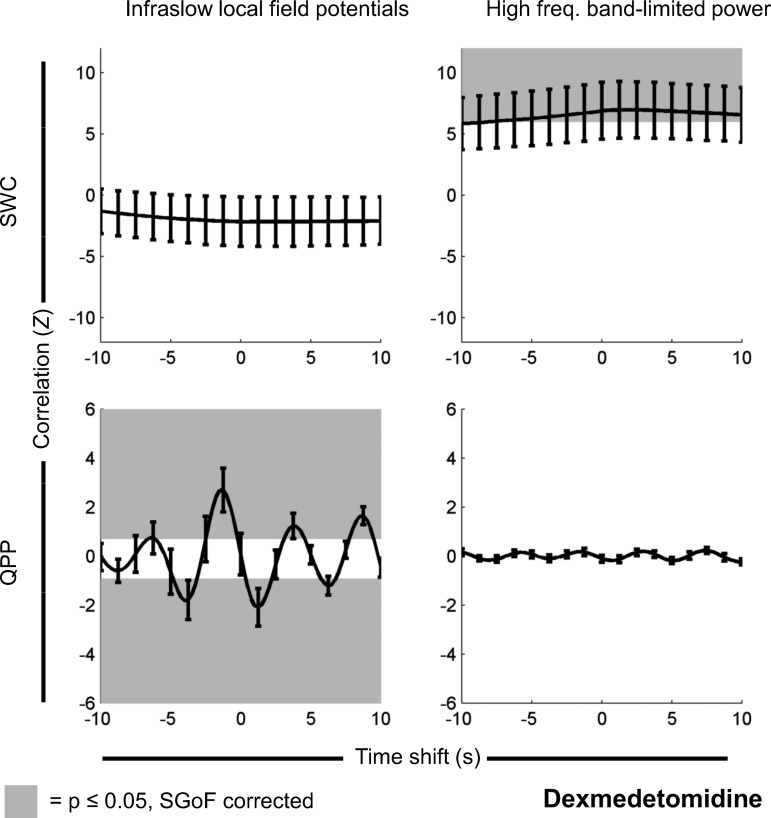
Fig. 4.
Same as Fig. 2, but for signals recorded under dexmedetomidine (n = 35 scans). There is significant correlation between SWC derived from rsfMRI and SWC derived from high-frequency BLP. There is also a significant correlation between the change in QPP strength over time and the infraslow LFP. However, the reverse pairings are not significant. Note that, for QPP, time shifts are arbitrary, and positive and negative correlations are expected (see Significance of QPP correlation vs. time shift in materials and methods). Partial correlation results had no statistically significant differences and appeared identical when plotted. As dexmedetomidine is the lightest anesthetic and close to an awake state, this suggests that different types of dynamic rsfMRI may reflect different frequency bands in the underlying electrophysiology, but deeper anesthesia (Figs. 2 and 3) obscures this.