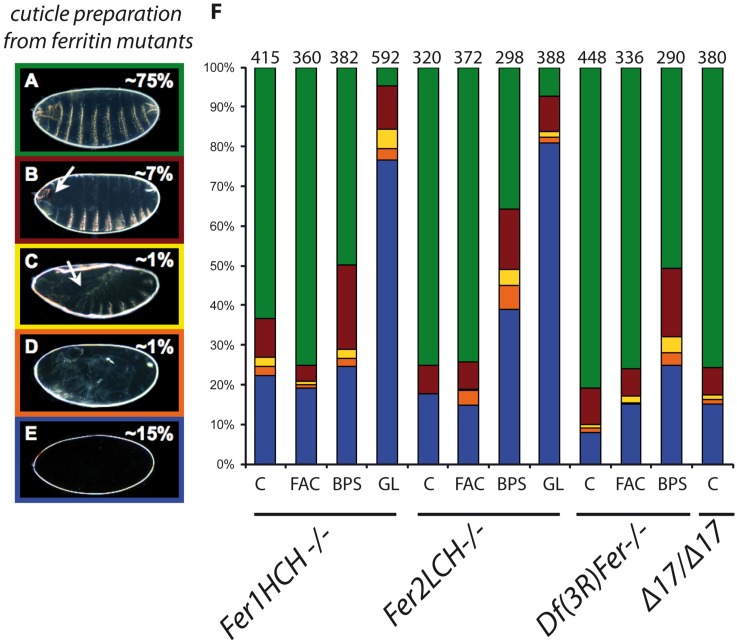
Fig 1. Ferritin mutants result in a variety of cuticle phenotypes quantified by different colors.
Examples are shown of (A) wild type cuticle (green), (B) head involution defects (red), (C) dorsal closure defects (yellow), (D) germ band retraction defects (orange), and (E) no cuticle deposition (blue). (F) Percentages of cuticular phenotypes of ferritin mutants. An enhancement of the earlier phenotypes was seen in mutant embryos whose mothers were fed BPS, which was dramatic in embryos derived from ferritin mutant germline clones. C: normal diet, FAC: high iron diet, BPS: low iron diet, GL: germline clones, n: number of embryos examined per genotype. An asterisk denotes statistical difference compared to the control lane at p<0.001.