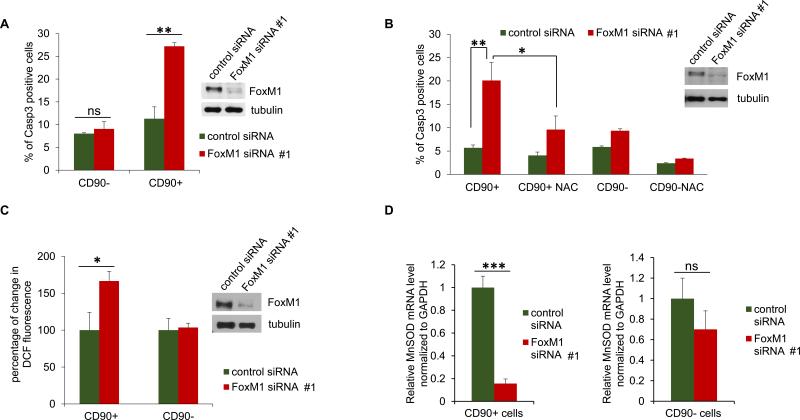
Fig. 7. Depletion of FoxM1 causes ROS-dependent apoptosis of CD90+ HCC cells.
Huh7 cells were transfected with control or FoxM1-siRNA #1 (all panels). Forty-eight hours after transfection, the cells were incubated with PE-tagged CD90-ab and FITC-tagged active caspase 3 detection reagent followed by separation of the CD90+ and active caspase 3 + cells using a cell sorter. Active Caspase 3+ CD90 + and the active caspase 3+ CD90- cells are plotted (A). (B) Twenty-four hours after siRNA transfection, the cells were treated with N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) for 24h followed by incubation with PE-tagged CD90-ab and FITC-tagged active caspase 3-detection reagent. The CD90+ and active caspase 3 + cells were quantified using a cell sorter. (C) Forty-eight hours after transfection, the cells were incubated with PE-tagged CD90-ab and DCF-DA followed by separation of the CD90+ and CD90- cells using a cell sorter. (D) Forty-eight hours after transfection, the cells were incubated with PE-tagged CD90-ab followed by separation of the CD90+ and the CD90- cells using a cell sorter. Total RNAs isolated from the fractionated cells were analyzed for MnSOD mRNA expression by quantitative RT-PCR. Statistically significant changes were indicated with asterisks (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01, ***, p<0.001.)