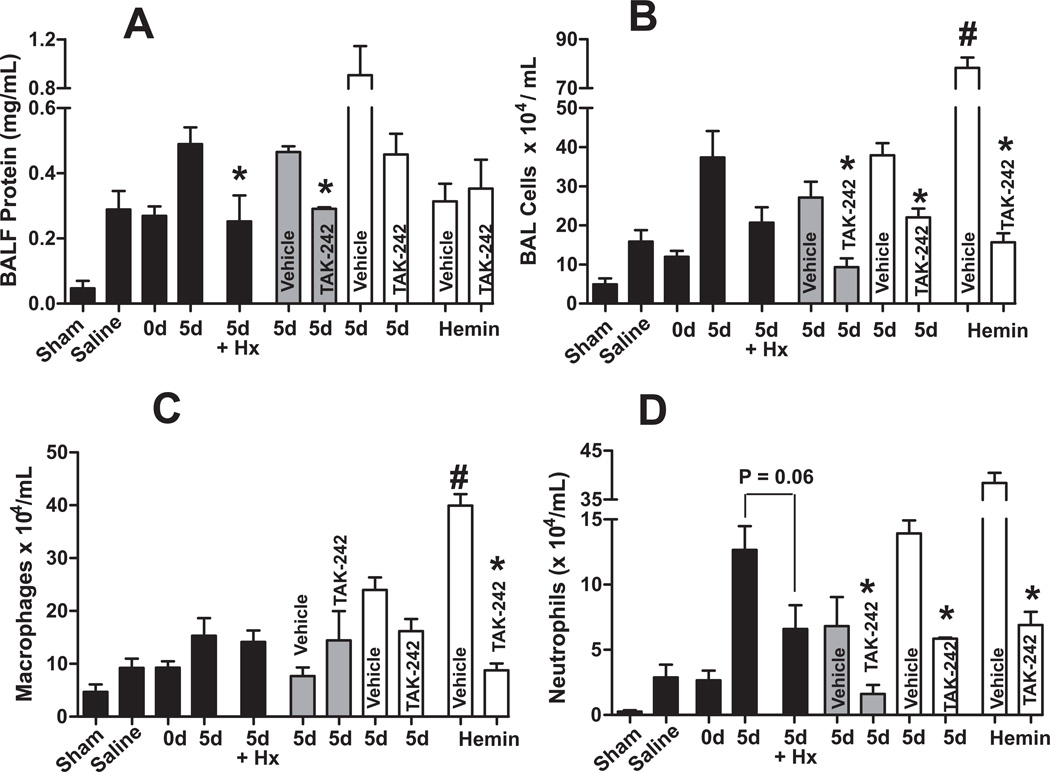
Figure 7. Role of free-heme in stored RBC mediated acute lung injury after trauma-hemorrhage.
Mice were exposed to trauma-hemorrhage and resuscitated with either saline or pRBC that were stored for either 0d or 5d, or hemin (15µM stock, 100µl transfusion) and BAL levels of protein (Panel A) or inflammatory cell accumulation (Panel B), with differential analysis (Panel C–D) determined. Hemopexin (Hx), intralipid (vehicle) or TAK-242 (TLR-4 inhibitor) therapy was administered once prior to hemorrhage (grey bars) or once 5–10 min prior to resuscitation (white bars). Note black bars are the same as data presented in Figure 5 and plotted here to allow comparison of TLR-4 inhibition and hemin effects to saline and RBC-dependent acute lung injury. *P<0.05 relative to respective vehicle by t-test. #P<0.05 by t-test relative to saline (N= 3–12 per group).