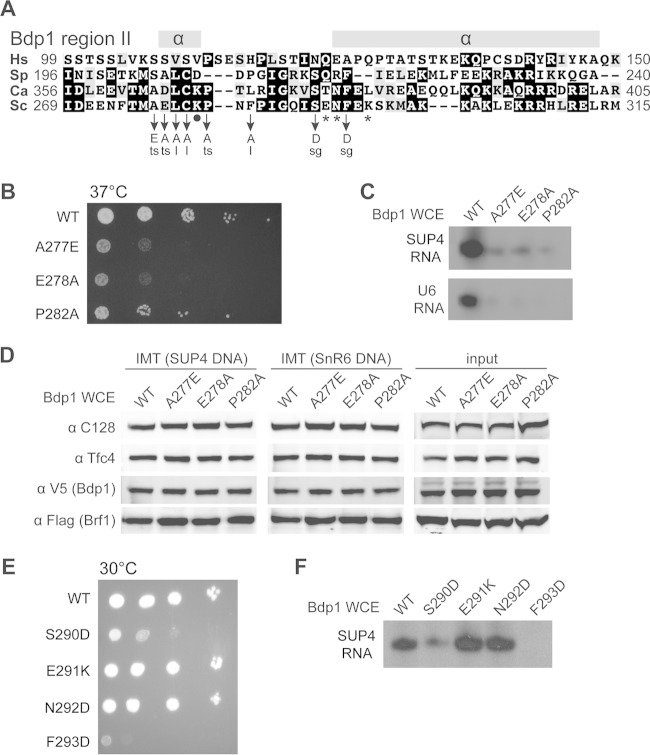
FIG 3.
Functional analysis of Bdp1 region II. (A) Bdp1 region II multiple-sequence alignment. As depicted in Fig. 1A, region II of Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Sc) Bdp1 ranges from amino acids 269 to 315. Hs, Homo sapiens; Sp, Schizosaccharomyces pombe; Ca, Candida albicans. The secondary structure of region II was predicted by use of the PSIPRED protein analysis workbench (http://bioinf.cs.ucl.ac.uk/psipred/). Symbols below the sequence alignment: asterisks, residues with BPA-cross-linking to C128; dot, the residue with BPA-cross-linking to Brf1. Point mutations and associated cell growth phenotypes are listed below. ts, temperature-sensitive (37°C) phenotype; sg, slow growth at all temperatures (16, 25, 30, and 37°C); l, amino acid substitution causing lethality. (B) Cell growth analysis of mutants with mutations in Bdp1 region II residues flanking the Brf1 BPA-cross-linking site. The three mutations caused a temperature-sensitive phenotype, as shown by serial dilution cell growth at 37°C. (C) In vitro transcription analysis for Bdp1 region II mutations flanking the residue cross-linking to Brf1. The autoradiograms show RNAs generated from the PICs of the IMT assay. As indicated, whole-cell extracts containing either WT or Bdp1 mutants were utilized in the in vitro transcription analysis. (D) PIC formation analysis of Bdp1 region II mutants. As indicated, Bdp1 mutant or WT whole-cell extracts were used in the IMT assay to isolate PICs on DNAs containing the SUP4 or SnR6 (U6) gene. Individual proteins of the isolated PICs were probed with antibodies, as indicated, in the Western blot analysis. (E) Cell growth analysis of mutations in Bdp1 region II residues involved in the C128 interaction. Representative slow cell growth at 30°C is shown. (F) In vitro transcription analysis for mutations in Bdp1 region II residues involved in the C128 interaction. The autoradiogram shows SUP4 tRNA from an in vitro transcription assay using WT or Bdp1 mutant whole-cell extracts.