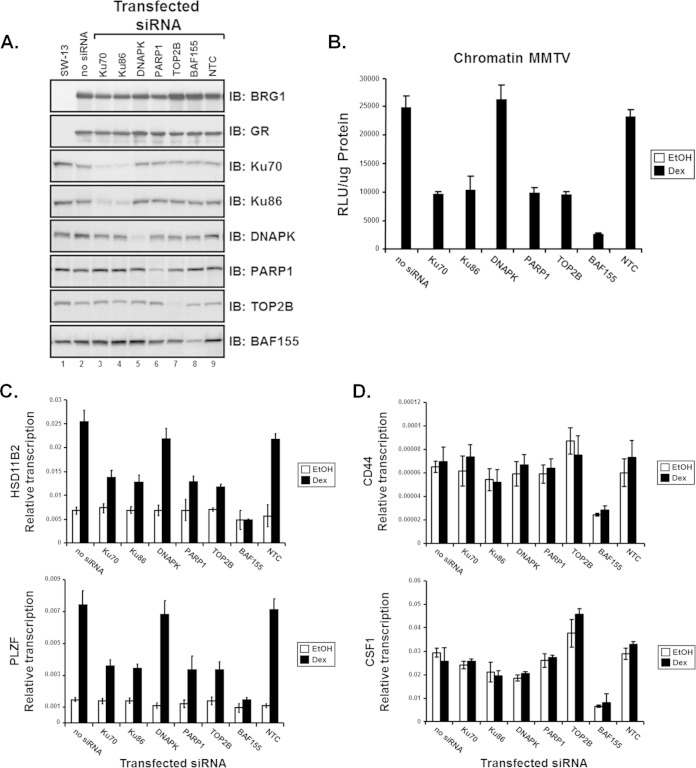
FIG 4.
Components of the TOP2β/PARP-1 complex are required for the transcriptional activation of chromatin MMTV and endogenous GR-mediated BRG1-dependent genes. siRNA duplexes specific for members of the TOP2β/PARP-1 complex were used to evaluate the requirement of Ku70, Ku86, DNAPK, TOP2β, and PARP-1 proteins in GR-mediated BRG1-dependent transcriptional activation. (A) Western blot analysis was used to monitor levels of protein expression of transfected plasmids and to evaluate the extent of protein knockdown upon introduction of siRNA. Total protein lysates from transfected SW-13 cells were resolved by SDS-PAGE and Western analysis performed using antibodies specific for BRG1, GR, Ku70, Ku86, DNAPK, PARP1, TOB2β, or BAF155. (B) SW-13/MMTV cells cotransfected with GR and BRG1 expression plasmids and the indicated siRNA were treated with 100 nM Dex or vehicle (EtOH) and assayed for luciferase activity. Relative MMTV luciferase activity was normalized to total protein measured and represented as relative light units (RLU). (C and D) Reverse transcription–real-time PCR analysis was used to determine expression levels of endogenous BRG1-mediated and GR-dependent (C) or -independent (D) genes in SW-13 cells upon siRNA protein knockdown. Total RNA, extracted from Dex- or vehicle-treated cells cotransfected with GR and BRG1 expression vectors and siRNA duplexes, was used as the template for cDNA synthesis. Equal amounts of cDNA were used for real-time PCR analysis with primers specific for GR-dependent genes HSD11B2 or PLZF (C) or GR-independent genes CD44 and CSF1 (D). Quantitative analysis was performed with data normalized to GAPDH, and results are displayed as relative transcription. A nontargeting control (NTC) siRNA used as a negative control for protein knockdown. Values are shown as mean ± standard deviation from 3 biological replicates.