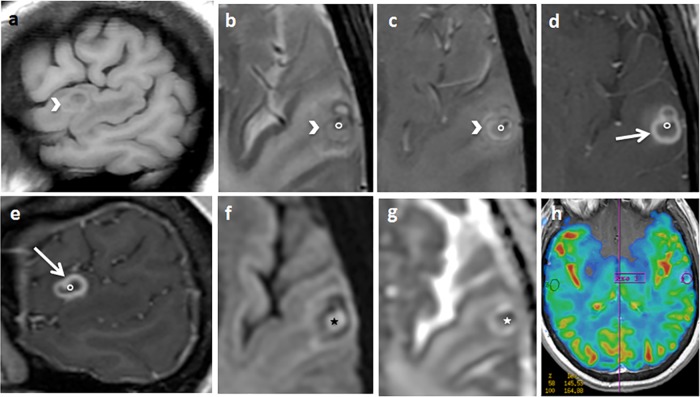
FIG 2.
Sagittal T1 (a), axial T2 spin echo (SE) (b), T2 star-weighted angiography (SWAN) (c), axial (d) and sagittal (e) T1 SE after gadolinium injection, axial diffusion (f), an apparent diffusion coefficient map (g), and a cerebral blood volume map (h). An arrow indicates a left temporal cortical annular enhancing lesion. The border of the lesion is thick and partially spontaneously hyperintense on T1 and hypointense on T2, with T2 SWAN suggesting the presence of hemosiderin or calcium deposits (arrowhead). The contrast enhancement is predominant in the inner part of the border (arrow). The center of the lesion appears hyperintense on diffusion-weighted MRI, with restriction of the diffusion coefficient suggesting thick content (star). In the center of the lesion, there is a small enhancing nodule attached to the border, hypointense on T2 SWAN (circle). The cerebral blood volume is diminished (h). Significant perilesional edema is revealed.