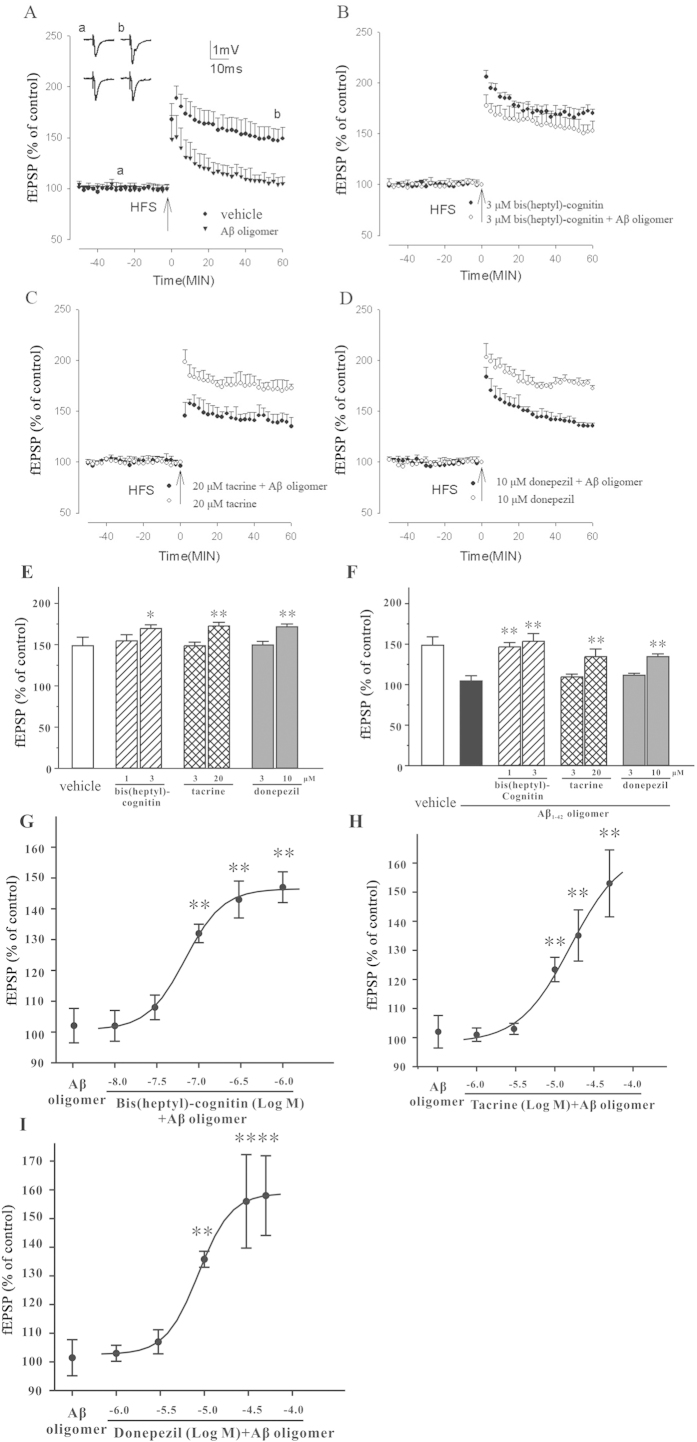
Figure 1. Bis(heptyl)-cognitin, but not other AChE inhibitors, enhances HFS-induced LTP, and prevents Aβ oligomers-induced inhibition of LTP at low concentrations.
(A) Aβ1-42 oligomers inhibit HFS-induced LTP. The graph shows the induction of LTP by vehicle (filled circles) or by 0.5 μM Aβ1-42 oligomers, perfused for 45 min prior to HFS (filled triangle). (B-D) Bis(heptyl)-cognitin (3 μM), tacrine (20 μM) and donepezil (10 μM) enhance HFS-induced LTP, and prevent Aβ1-42 oligomers-induced inhibition of LTP. Bis(heptyl)-cognitin, tacrine and donepezil were perfused over the slices for 60 min prior to HFS. (E) Bis(heptyl)-cognitin (3 μM), tacrine (20 μM) and donepezil (10 μM) enhance HFS-induced LTP. (F) Bis(heptyl)-cognitin (3 μM), tacrine (20 μM) and donepezil (10 μM) prevent Aβ1-42 oligomers-induced inhibition of LTP. Bis(heptyl)-cognitin, tacrine and donepezil were perfused over the slices for 60 min prior to HFS. After 15 min, Aβ1-42 oligomers were perfused. (G-I) The concentration-dependent effects of bis(heptyl)-cognitin (G), tacrine (H) or donepezil (I) on Aβ1-42 oligomers-induced inhibition of LTP. Data represent means ± SEM (n = 5). *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 vs. vehicle group in (E); and **p < 0.01 vs. Aβ1-42 oligomers group in (F-I) (ANOVA and Tukey’s test).