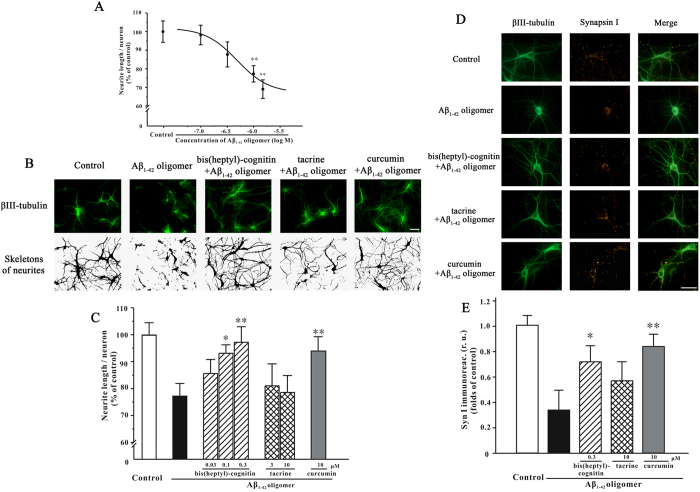
Figure 3. Bis(heptyl)-cognitin, but not tacrine, prevents Aβ1-42 oligomers-induced synaptotoxicity in primary mature hippocampal neurons.
(A) Aβ1-42 oligomers reduce neurite length in hippocampal neurons. After DIV14, hippocampal neurons were treated for 4 d with various concentrations of Aβ1-42 oligomers prior to fixation and analysis for the length of βIII-tubulin positive neurites by using NeuriteTracer program. (B) Hippocampal neurons were pre-incubated with 0.3 μM bis(heptyl)-cognitin, 10 μM tacrine or 10 μM curcumin, and exposed to 1 μM Aβ1-42 oligomers 2 h later. Four days after Aβ1-42 oligomers challenge, neurons were fixed. Upper: Neuronal cultures were stained with anti-βIII-tubulin antibody. Lower: βIII-tubulin positive neurites were digitally identified and skeletonized for quantification by NeuriteTracer program (scale bar: 10 μM). (C) Hippocampal neurons were pre-incubated with various treatments as indicated and exposed to 1 μM Aβ1-42 oligomers 2 h later. Four days after Aβ1-42 oligomers challenge, neurons were fixed and analyzed for the length of βIII-tubulin positive neurites by using NeuriteTracer program. (D) Hippocampal neurons were pre-incubated with 0.3 μM bis(heptyl)-cognitin, 10 μM tacrine or 10 μM curcumin and exposed to 1 μM Aβ1-42 oligomers 2 h later. Four days after Aβ1-42 oligomers challenge, neurons were fixed and labeled with βIII-tubulin and synapsin I antibodies (scale bar: 10 μM). (E) Synapsin I integrated immunofluorescence intensity was evaluated by using ImageJ. r.u.: relative unit. Data represent means ± SEM (5 images were analyzed in each group), **p < 0.01 vs. control in (A); *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 vs. Aβ1-42 oligomers group in (C) and (E) (ANOVA and Dunnett’s test).