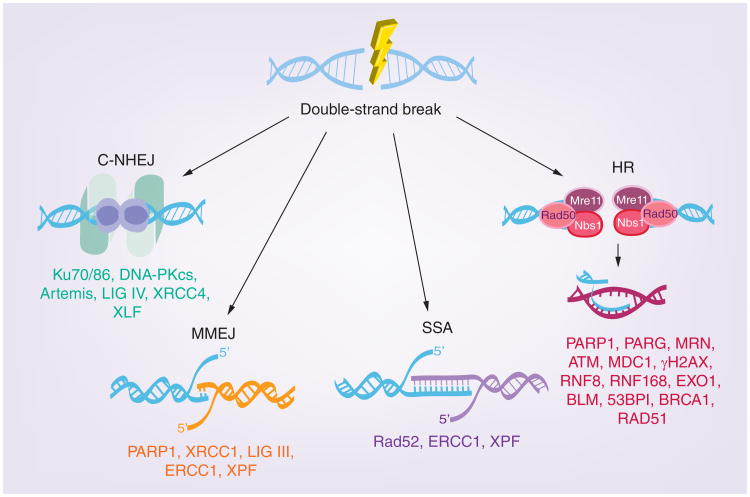
Figure 1. DNA double-strand break repair pathways.
In response to double-strand breaks, DNA can be repaired by one of four major pathways: C-NHEJ, MMEJ, SSA and HR. HR, SSA and MMEJ are homology-directed forms of repair; whereas, C-NHEJ does not require homology. Double-strand breaks arising at replication forks can also be repaired by synthesis-dependent strand annealing and break-induced repair mechanisms via ATR-CHK1 signaling (not shown in figure).
C-NHEJ: Classic nonhomologous end joining; HR: Homologous recombination;
MMEJ: Microhomology-mediated end joining; SSA: Single strand annealing.