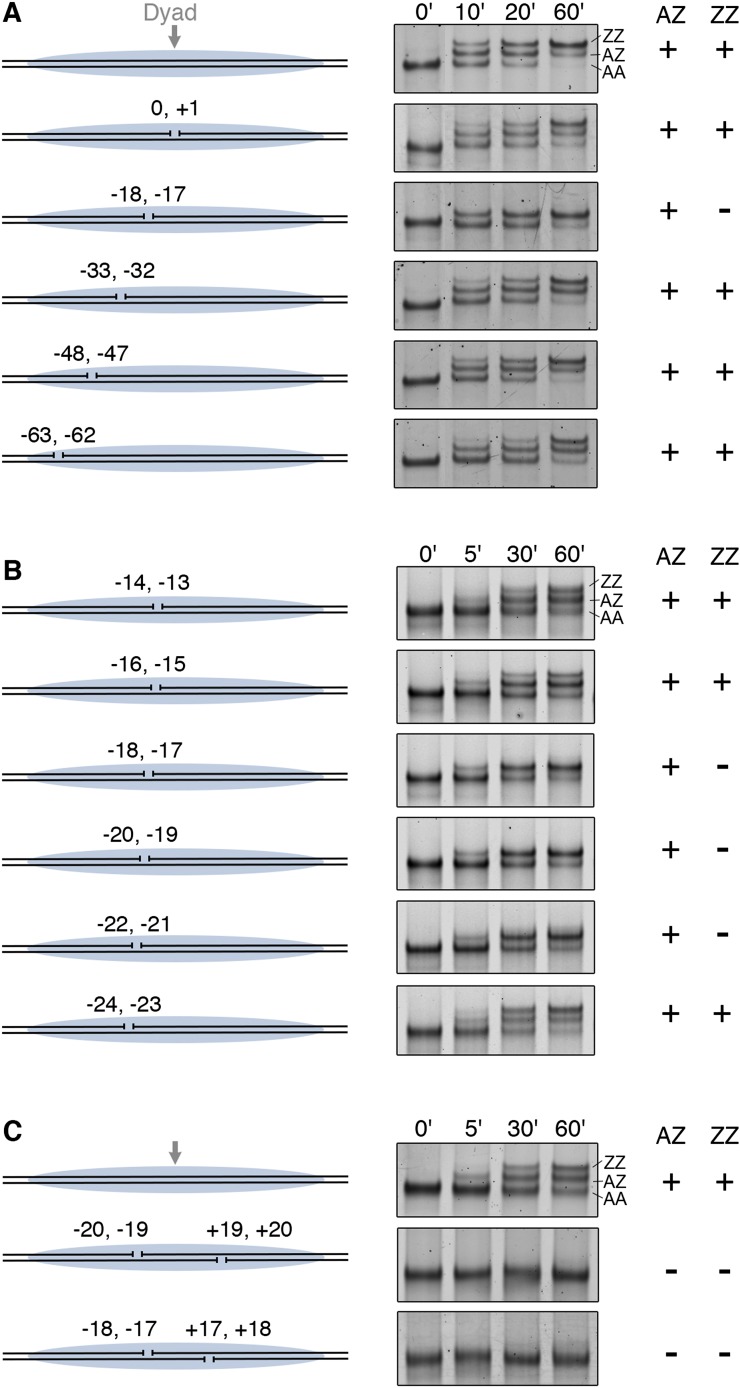
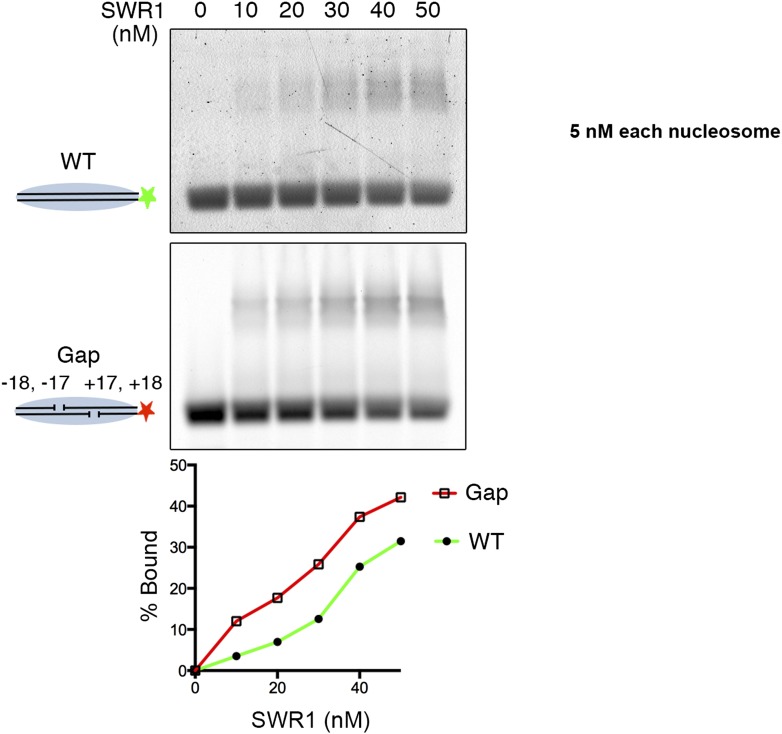
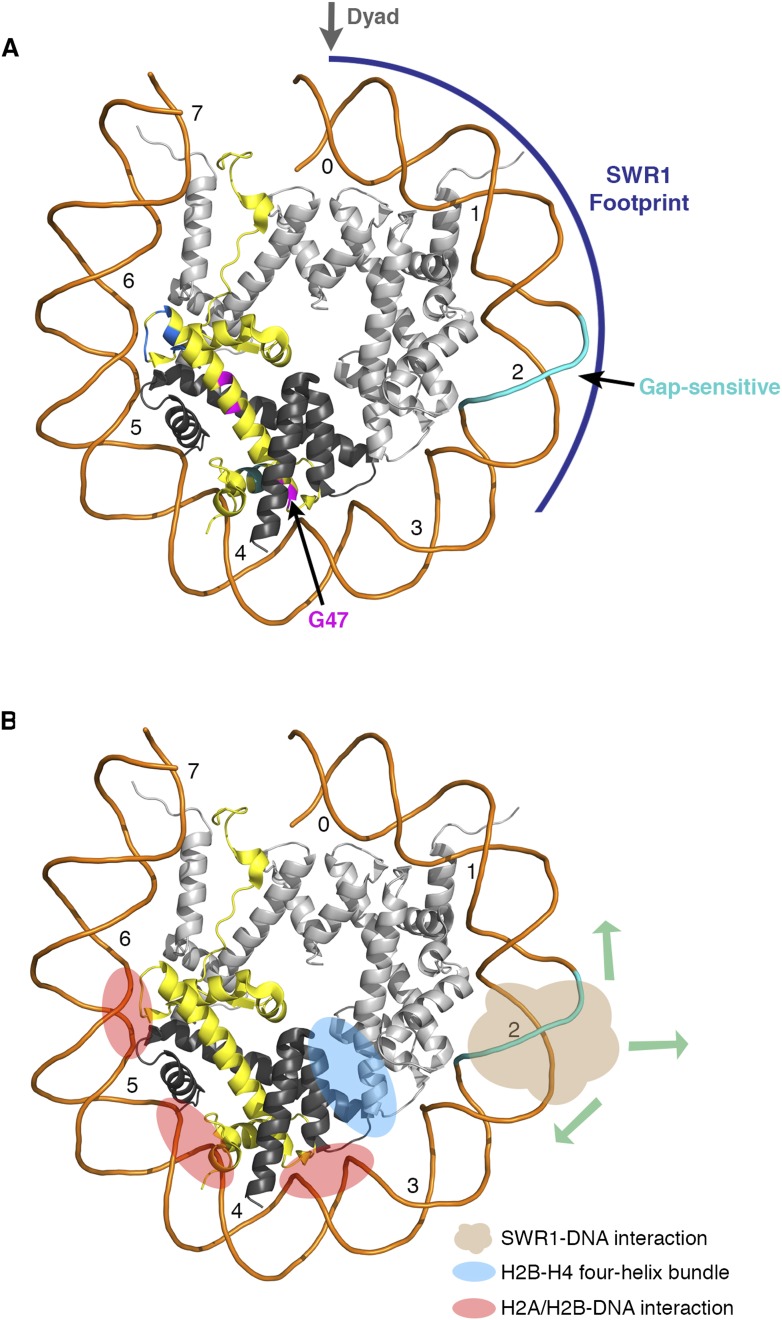
Figure 3. DNA gaps block SWR1 activity when positioned 17–22 bp on either side from dyad.
All nucleosomes have a 20 bp linker DNA at both ends, and a two-nucleotide gap introduced at indicated positions. EMSA (6% native PAGE) shows the H2A.Z replacement reaction, terminated at the indicated times, using fluorescently labeled nucleosomes (4 nM), SWR1 (2 nM), and H2A.Z-3F-H2B dimer (10 nM). Nucleosome products with 0, 1, and 2 H2A.Z-3FLAG molecules are resolved (AA, AZ, ZZ). (A) Mapping of gap sites that block SWR1 activity. Left: Design of WT and gap nucleosomes. Right: (+) and (−) denote presence and absence of the AZ or ZZ species. (B) Fine mapping of the gap-sensitive region near two turns from nucleosome dyad. (C) Gaps within the sensitive region on both sides of nucleosome completely block SWR1 activity.