Figure 1.
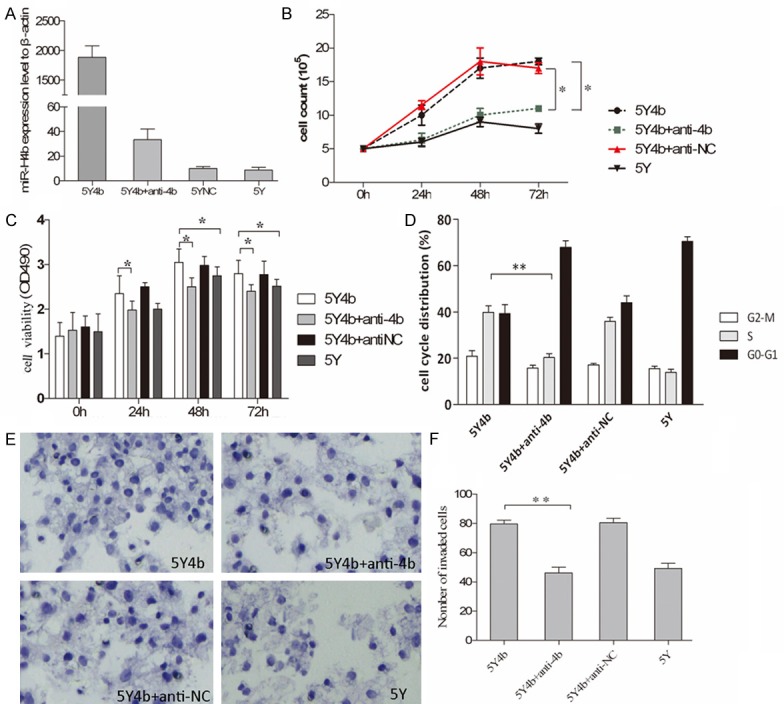
miR-4b promotes cell proliferation, invasion and cell cycle progression. A. qPCR analysis of the expression levels of miR-H4b in 5Y or 5Y4b cells. Anti-4b nucleotides were transfected into 5Y4b cells to detect its downregulation role on miR-4b. The expression values of β-actin are set at 1 and the relative expression levels of miR-H4b were determined by using the 2-ΔΔCt method. B. Proliferation of 5Y4b cells was measured by cell counting assay after transfecting either anti-4b or scramble anti-NC. The cell proliferation was determined by cell counting 0, 24, 48 and 72 h following transfection. The results are presented as the mean number of cell lines at different time points. The experiment was performed in triplicate. Anti-4b interfering RNA decreased the proliferation capacity of 5Y4b cells. C. Cell viability was measured by the MTT assay post 0 h, 24 h, 48 h, 72 h of transfection. The histogram shows mean values of A490 from three independent experiments. Anti-4b or anti-NC were transfected into 5Y4b cell separately. Compared to 5Y4b cells, cell viability of 5Y cells and 5Y4b cells with anti-4b was dramatically decreased. *P<0.05. D. The proportion of 5Y4b cells stayed in S-phase was lager than 5Y cells. 5Y4b cells transfected with anti-4b or anti-NC were subjected to cell cycle analysis. *P<0.05. **P<0.01. E. miR-4b increased the invasive capacity of 5Y cells. 5Y cells, 5Y4b cells transfected with anti-4b or anti-NC were loaded into the Matrigel-coated upper chambers of Transwell plates. Cells were counted under a microscope in five random fields at ×200 magnification. F. The compelling number of invaded cell was illustrated in histogram. *P<0.05, 5Y4b cells vs. 5Y4b cells with anti-4b.
