Figure 2.
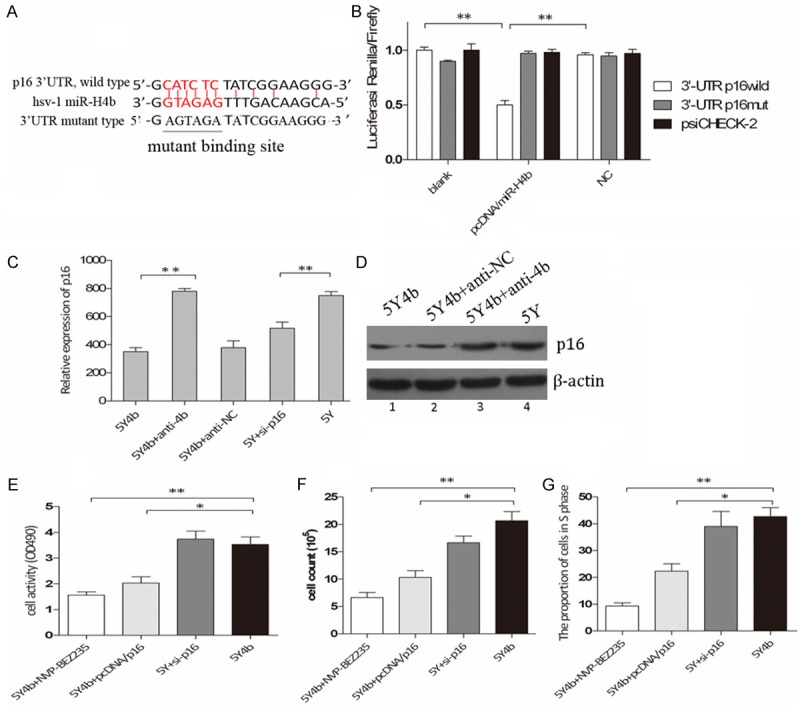
CDKN2A is target of miR-H4b. A. MiR-H4b target site resides at nucleotides of the p16 3’-UTR. Binding sites are indicated in red letters and the corresponding mutants are labeled in a solid line. All the complementary pairing bases are indicated in the vertical curve. B. Luciferase activity assay for direct targeting of the 3’-UTR of p16 by miR-H4b. Two copies of wild-type and mutant miR-H4b target sequences of p16 were fused with luciferase reporter and respectively co-transfected into HEK 293 cells with recombinant plasmid containing miR-4b precursor, and luciferase activity measured 48 hours post transfection. **P<0.01. C. P16 mRNA levels analyzed in 5Y4b cells tranfected with anti-4b by qRT–PCR; D. P16 protein levels analyzed by western blot. P16 expression was lower in 5Y4b with or without anti-NC cells compared with 5Y or 5Y4b cells with anti-4b. Similar results were observed in cells cotransfected with siRNA for p16 into 5Y cells. E. Promoting proliferation ability of miR-H4b mediated by inhibiting target genes p16. The cell viability of 5Y4b cells added with either NVP-BEZ235 at 1 nM for 60 h or pcDNA/p16 plasmids (without 3’-UTR binding sites) was much lower than that of 5Y4b cells or 5Y cells with siRNA for p16. F. Proliferation of cells in different groups was measured by cell counting assay. NVP-BEZ235 and pcDNA/p16 in 5Y4b cells can effectively decrease the proliferation capacity compared to 5Y cells with si-p16. G. PcDNA/p16 and NVP-BEZ235 rescued the uncontrolled cell cycle, and 5Y4b cells or 5Y cells with si-p16 showed a higher proportion of cells in s phase than other groups. **P<0.01.
