Figure 3.
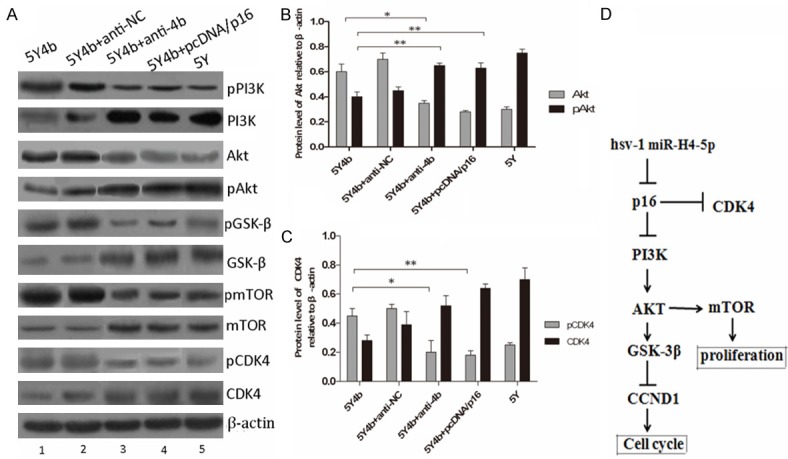
miR-H4b inhibits PI3K-AKT and mTOR pathways by targeting p16. A. miR-H4b overexpression reduced the activity of PI3K and mTOR pathways in 5Y4b cells. Knockdown of miR-H4b by anti-4b increased the activity of PI3K and mTOR signaling in 5Y4b cells. PcDNA/p16 plasmids were transfected into 5Y4b cells to investigate whether re-expression of p16 can rescue these effects. PI3K-AKT-(GSK-3β)-mediated pathway activity was measured by examining expression of phosphorylated AKT (pAKT), phosphorylated PI3K and phosphorylated GSK3β (pGSK3β), whereas PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway activity was measured by examining expression of mTOR and phosphorylated mTOR. Protein level of phosphorylated CDK4 decreased in 5Y4b cells after transfecting with anti-4b. B-C. The bar chart showed the ratio of Akt or pAkt and CDK4 or pCDK4 to β-actin at each group. These data are means ± SEM. (n=3, *P<0.05, **P<0.01). D. Schematic regulation of hsv-1 miR-H4-5p on PI3K-Akt pathway and Akt-mediated mTOR pathway. Arrows means promopting effect, and T type arrow means inhibiting effect on downstream.
