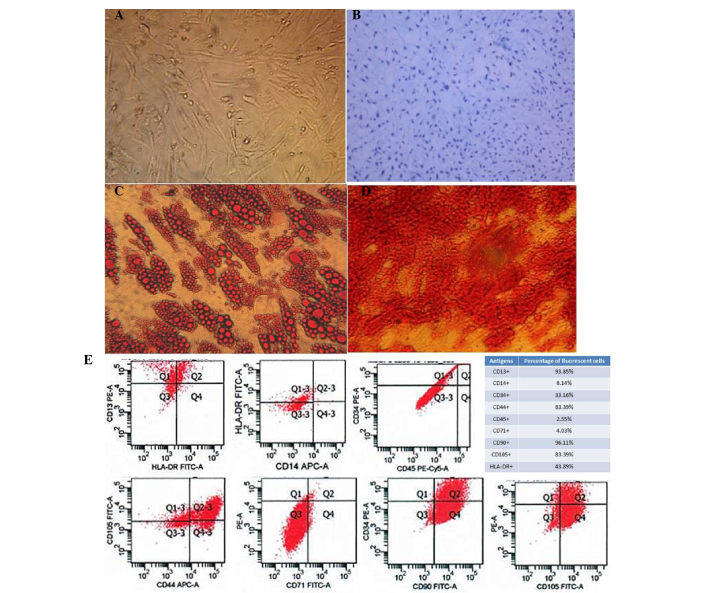
Figure 1.
Characterization of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (AD-MSCs). (A) A representative phase-contrast microscopy image of AD-MSCs showing typical spindle-shaped morphology (magnification, ×100). (B) Differentiation of cartilage cells (magnification, ×400). (C) Adipocyte differentiation (magnification, ×400). (D) Osteogenic differentiation of AD-MSCs stained with Alizarin Red (magnification, ×400). (E) Fluorescence-activated cell sorting characterization of AD-MSCs expressing CD13, CD90, CD44 and CD105, the commonly used surface markers for MSCs. MSCs were also shown to express CD14, CD34, CD45 and CD71 at a very low level. FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; PE, phycoerythrin.