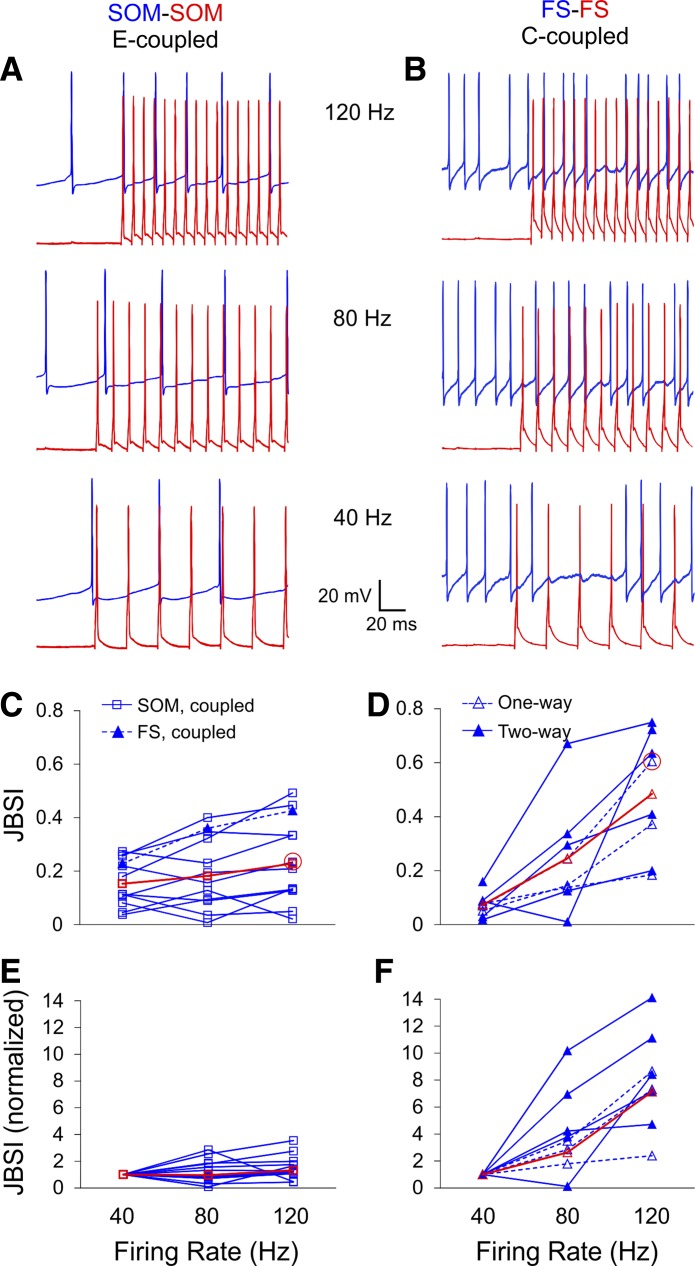
Fig. 5.
Chemically driven, but not electrically driven, synchrony is strongly firing rate dependent. A and B: firing at predefined rates (40, 80, 120 Hz) was elicited in the driver cell (red traces) by trains of 20 brief current pulses repeated every 3 s, and tonic firing was elicited in the follower cell (blue traces) by constant current injection. C and D: summary plots of JBSI at each firing rate for all pairs tested; red symbols are group averages. Data points corresponding to the 2 example pairs are circled in red. E and F: the same data normalized to the JBSI value at 40 Hz. Synchrony was strongly dependent on driver firing rate in C-coupled FS pairs (D and F) and only weakly so in E-coupled SOM pairs (C and E). One E-coupled FS pair (filled triangles) is included with the SOM pairs in C; it resembled E-coupled SOM pairs rather than C-coupled FS pairs.