Fig. 3.
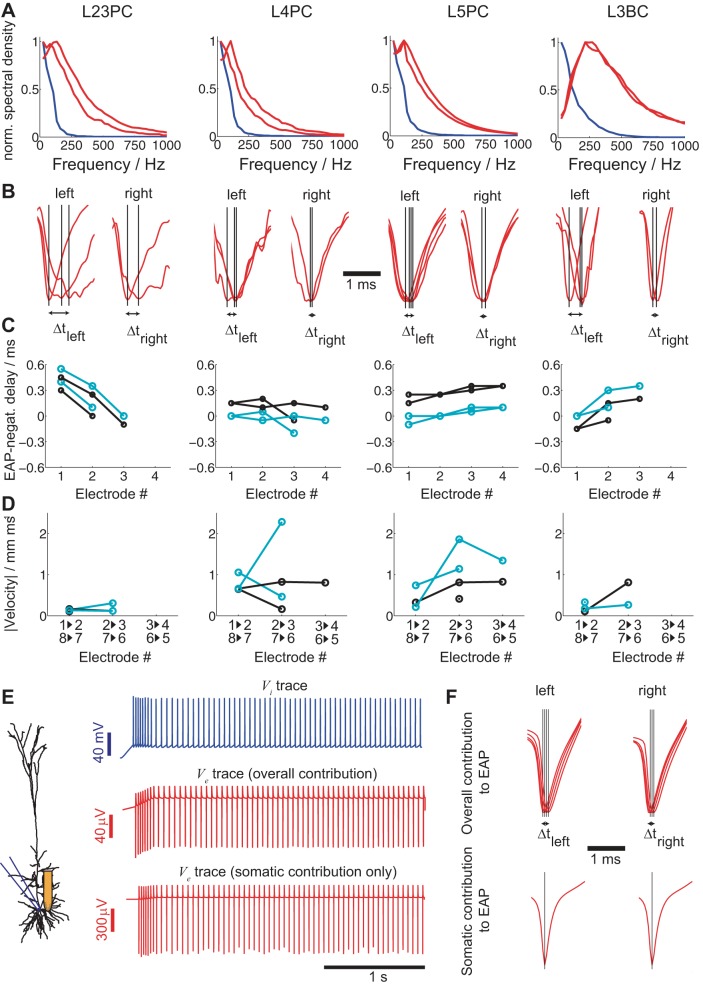
Temporal characteristics of EAP signals from identified single neurons. A: frequency spectra of intracellular spikes (blue lines) and the 2 largest EAPs (red lines) of the 4 neurons shown in the figure. B: alignment of the mean EAP signals from the 8 sites along the silicon shank closest to the cell body to the spike initiation time tspike (determined intracellularly) reveals temporal differences between the EAP signals (left to right). C: time difference between the EAP minimum at different sites along the same shank and the intracellular spike onset (black) or the time of the EAP negativity of the electrode recording the strongest EAP (cyan). The 2 shank sides are considered separately (see Fig. 2, A–D, 2nd and 3rd columns), hence the multiple lines (x-axis: electrode number as defined in Fig. 2A). D: signal-propagation velocity v calculated from the interelectrode distances (x-axis: electrodes involved in calculation of v). AP minima delays are attributed to somatic APs traveling back along the apical dendrites (see text). E: same intracellular input as in Fig. 1 delivered to the soma of a L5 pyramidal neuron simulation (see materials and methods) with extracellular recording sites positioned at the same locations as for the silicon probe (left) and the resulting intra (top)- and extracellular responses (middle and bottom). Ve at a site 30 μm from the soma is either computed by taking into consideration the entire neuron (middle) or only the soma (bottom). F: if the same analysis as in B is carried out for the simulated data, the temporal differences between the EAP signals along the same shank can be attributed to membrane currents along the whole neural morphology (top). (Notably, the EAP delay and propagation speed are very similar to the ones measured experimentally for the L5 pyramidal neuron in B and C.) An identical simulation with only somatic compartments contributing to the EAP reveals no temporal differences (bottom).