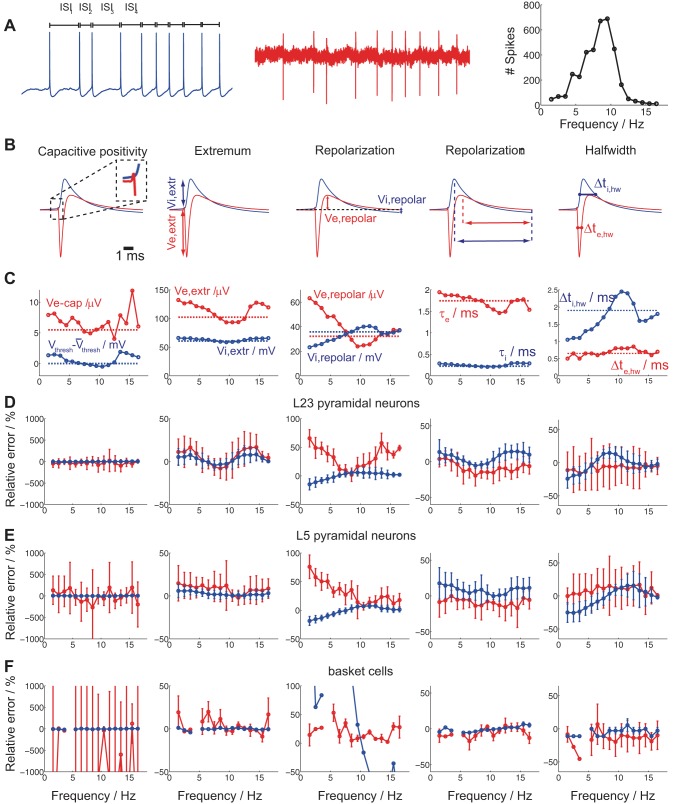
Fig. 4.
Cell type-specific intra- and extracellular spike-waveform characteristics as a function of spike frequency. A: intracellular somatic DC current injection of varying strength results in intracellularly (blue) and extracellularly (red) recorded spikes. Spike frequency is defined for each spike as the inverse of its ISI resulting in a Gaussian-like spike frequency histogram (right). B: 5 extracellular spike-waveform characteristics were studied (left to right): the initial capacitive positivity (Ve,cap) amplitude, the EAP negativity amplitude (Ve,extr), the EAP repolarization positive (Ve,repol) amplitude, the EAP repolarization time τe, and the EAP half-width Δte,hw (features designated in red). Likewise, 5 intracellular spike waveform characteristics were analyzed (left to right): change in voltage spike threshold compared with the mean, the intracellular spike-amplitude (Vi,extr), the intracellular postspike negativity (Vi,repol) amplitude (compared to baseline), the intracellular spike repolarization time τi, and the intracellular spike half-width Δti,hw (features designated in blue). C: intra- (solid blue)- and extracellular (solid red) spike-waveform characteristics as a function of spike frequency for the L5 pyramidal neuron in A. Broken lines indicate the mean of each intra- and extracellular spike-feature across spike frequencies. D–F: differences in intra- and extracellular spike waveform characteristics (C) as a function of spike frequency with reference to the mean waveform across all spikes irrespective of spike frequency for 8 L23 (D) and 12 L5 (E) pyramidal neuron recordings as well as 4 basket cell (F) recordings (red: extracellullar feature; blue: intracellular features; circles: mean; error bars: SD). Differences are expressed as the relative error (for more thorough explanation, see text). Ve,extr variability is consistently larger than Vi,extr variability for all cell types (2nd and 3rd columns; basket cell variability in the 3rd column, in blue, is attributed to repolarization being very close to baseline) while temporal feature variability much less so (4th and 5th column).