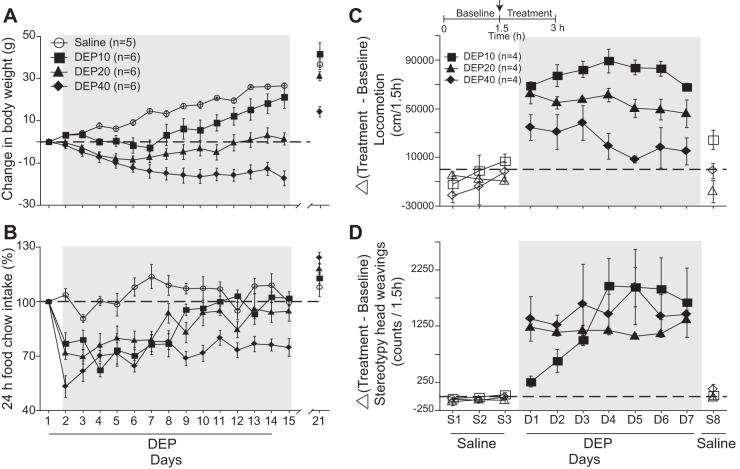
Fig. 1.
Effects of diethylpropion (DEP) on weight loss, feeding, locomotion, and stereotypic head movements. A: the change in body weight of control rats daily injected intraperitoneally with saline (○) from day 1 to day 14 compared with rats injected with DEP at 10 (■), 20 (▲), and 40 mg/kg (⧫) (hereafter DEP10, DEP20, and DEP40, respectively). Gray shading depicts the change in body weight measured 20 min before each DEP injection. The break in the axis indicates where the treatment was stopped. The horizontal dotted line represents no weight change. B: the DEP-induced change in food intake for the same subjects shown in A. C: the effects of DEP10, DEP20, and DEP40 (Δ, change relative to baseline) on the animal's locomotion (in cm/1.5 h). This protocol consisted of 3 days of saline treatment (S1–S3), 7 days of DEP treatment (D1–D7) and 1 final day of saline treatment (S8). Inset displays the daily protocol. D: the DEP-induced effect on stereotypic head movements (counts/1.5 h). Symbols represent means ± SE, and the shading indicates treatment times.