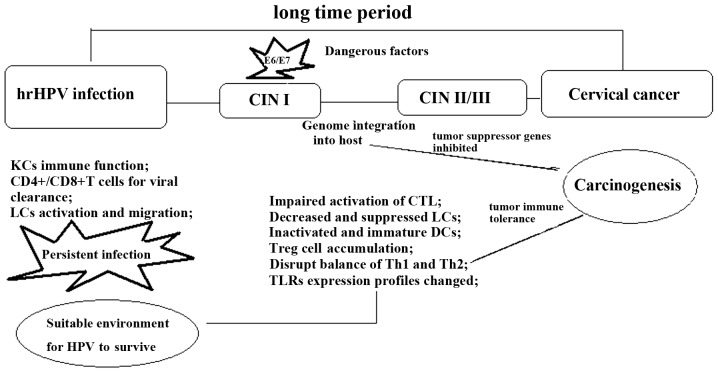
Figure 1.
There are several stages from HPV infection to cervical cancer. Immune system modification is the most important factor to promote lesion progression. Genome integration would initiate immune cell activation and differentiation profiles changes. These changes are characterized by the inactivated CD4+/CD8+ T cells, Treg cell upregulation, M2 cell generation, the immature DCs and reduced anti-inflammatory cytokine infiltration. hrHPV, high-risk human papilloma virus; CIN, cervical intraepithelial neoplasia; CD, cluster of differentiation; LC, Langerhans cell; CTL, cytotoxic T cell; DC, dendritic cell; Th, T-helper cell; TLR, toll-like receptor.