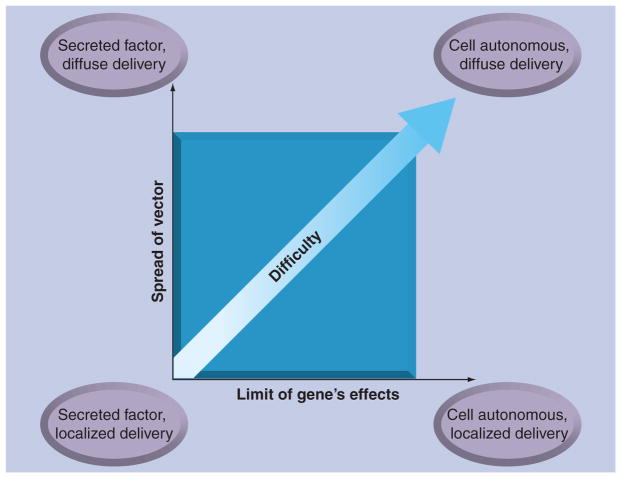
Figure 2. General categories of CNS gene delivery.
In a broad sense, the difficulty of a gene therapy for any given disease depends on three factors: the range of vector delivery that must be achieved, the range of therapeutic effect that the transgene will impart, and how much knowledge about the disease is available to guide the choice of transgene and the extent that regulation is necessary. In this regard, a localized therapy with a secreted factor represents the easiest therapeutic approach, while a cell-autonomous transgene requiring widespread efficient vector delivery represents the most difficult. The third dimension (not shown) to predict the success of a gene therapy approach for any given disease is the available data about the disease to guide the design of an appropriate therapeutic gene cassette.