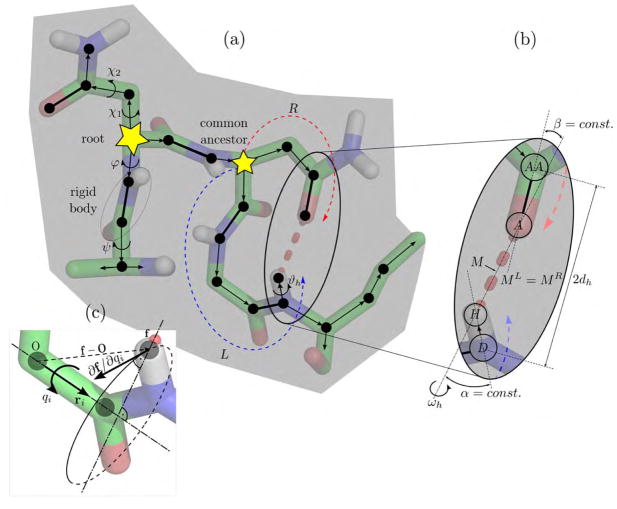
Figure 2.
Kinematic representation of a protein, green represents carbon atoms, red oxygen, blue nitrogen, and white hydrogen. (a) Directed kinematic spanning tree of a protein fragment. Edges (thin arrows) represent rotatable bonds, and vertices represent rigid groups of atoms. Individual atoms (black dots) that are connected via non-rotatable double covalent bonds (thick lines) are merged into a single rigid body. Starting from the root, each vertex is visited by a directed edge from its parent vertex. Hydrogen bonds constrain two branches leaving from a common ancestor at their end effectors. (b) Constraint parameterization. Changes in position of the hydrogen bond midpoint M along the left and the right branches have to match. The angles α and β are fixed, allowing a rotation ωh only around the hydrogen bond axis. (c) The partial derivative ∂f/∂qi required for the constraint Jacobian matrix is the cross-product ri × (f – O) and can be efficiently calculated.