Figure 5.
Selective ChR2-EYFP Expression in Histaminergic Neurons and Tracing Their Axons to Neocortex and Striatum
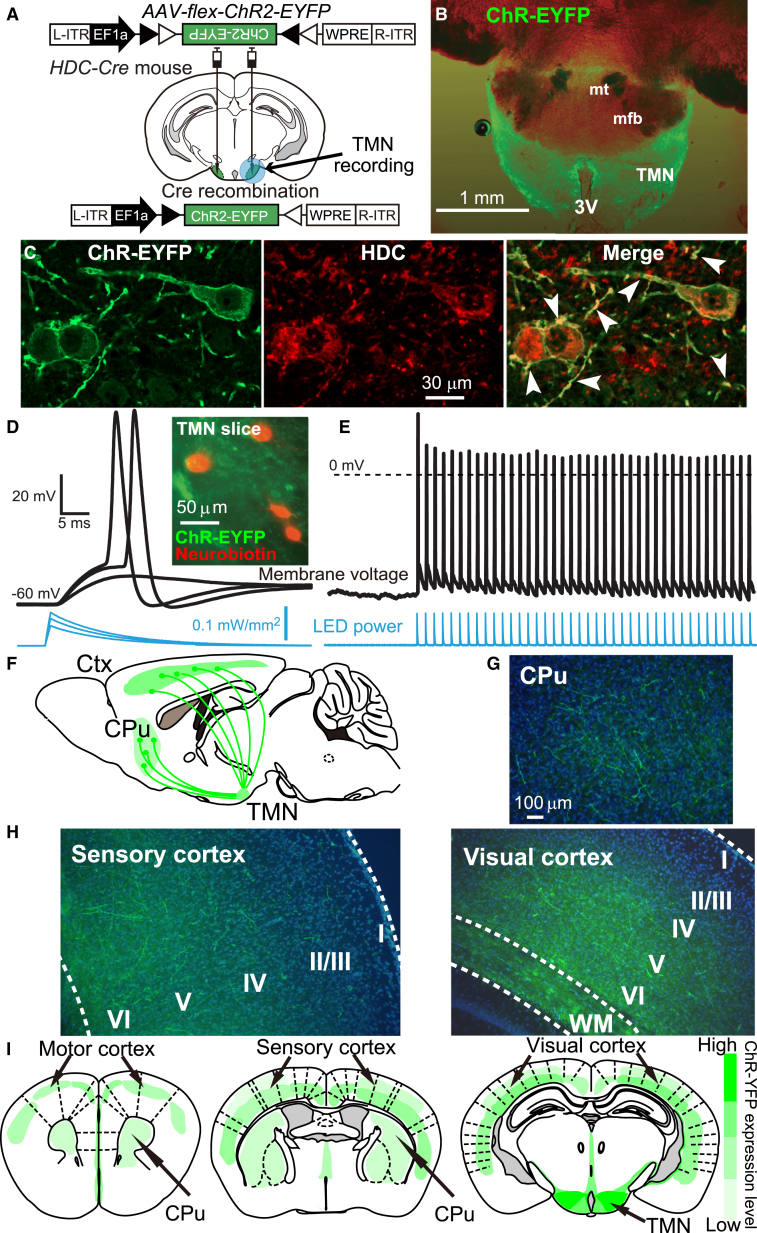
(A) AAV-flex-ChR2-EYFP was bilaterally injected into the TMN region of HDC-Cre mice. The blue circle indicates the area of the slice that was optically stimulated.
(B) Cre recombination produced ChR2-EYFP expression within HDC-expressing neurons. Shown is a combined bright-field and primary fluorescence photograph, taken at low magnification, of a freshly cut coronal brain slice used for electrophysiological recording from TMN neurons.
(C) ChR-EYFP expression in the TMN imaged with antisera to GFP (green) and HDC (red), with arrowheads indicating ChR2 expression in processes.
(D) The duration of the LED power output (blue trace) measured from the objective lens, and the membrane voltage recorded (black trace) from the soma of a HDC-ChR2-EYFP neuron. Increasing the LED power depolarized the membrane to generate action potentials. Inset image: four neurons recorded from this slice with cofluorescence for ChR-EYFP (green) and postrecording neurobiotin fill (red).
(E) The same cell as (D) firing action potentials with 5 Hz light stimulation.
(F) Schematic of the fibers (axons) which, following AAV-flex-ChR2-EYFP injection into the TMN of HDC-Cre mice, transported ChR-EYFP from the HDC-ChR2-EYFP soma into the neocortex and caudate-putamen.
(G and H) Low-power photographs of the ChR2-EYFP-positive fibers in the caudate-putamen (CPu) (G) and sensory and visual cortex (H). Blue, DAPI; I, layer I; II, layer II; III, layer III; IV, layer IV; V, layer V; VI, layer VI; WM, white matter.
(I) Schematic of the ChR2-EYFP fiber distribution in the caudate-putamen (CPu) and neocortex.