Figure 6. Model for interactions between HIF1α, ATF4 and p53 in the response to hypoxic stress.
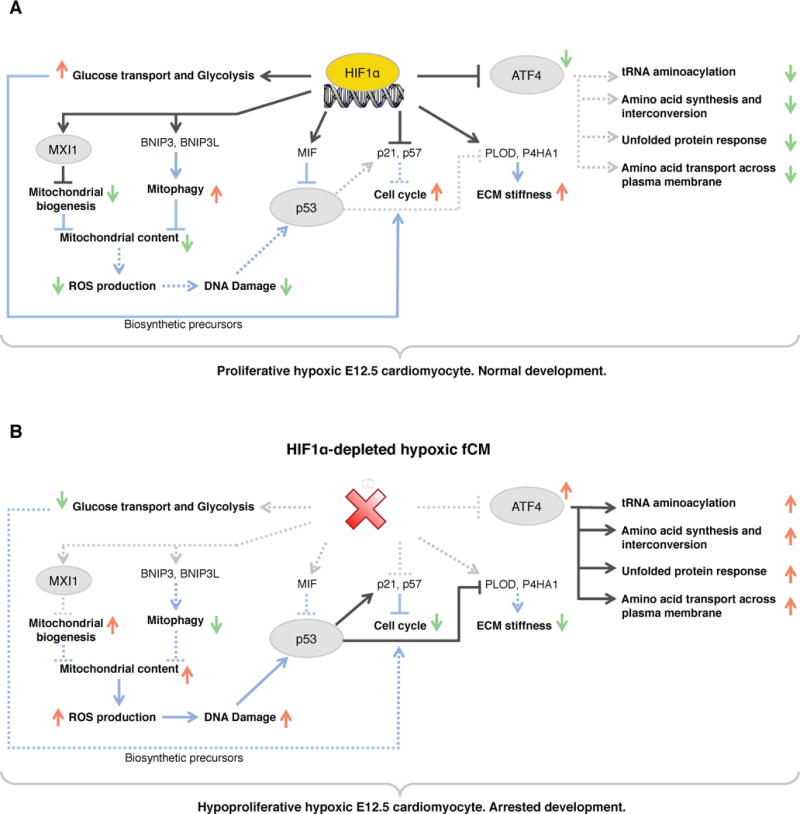
A) In hypoxic wild-type fCMs, HIF1α potentiates proliferation by regulating a myriad of cellular functions: carbohydrate metabolism, ECM deposition, OXPHOS, cell cycle, p53 and ATF4 signaling. B) In the absence of HIF1α, hypoxic fCMs failed to adapt their metabolism to low oxygen, ectopically activated ATF4 and p53 pathways and upregulated expression of inhibitors of cell cycle. As consequence, these cells adopted a quiescent phenotype that lead to arrested cardiac development. Red arrows represent upregulation and green arrows represent downregulation. TFs are circled and cellular processes are bold. Black lines represent transcriptional regulation and blue lines represent post-translational interactions or effects. Dashed lines represent inactive interactions. See Figure S5 for a detailed list of all genes involved in the cellular processes highlighted in this diagram.
