Fig. 2.
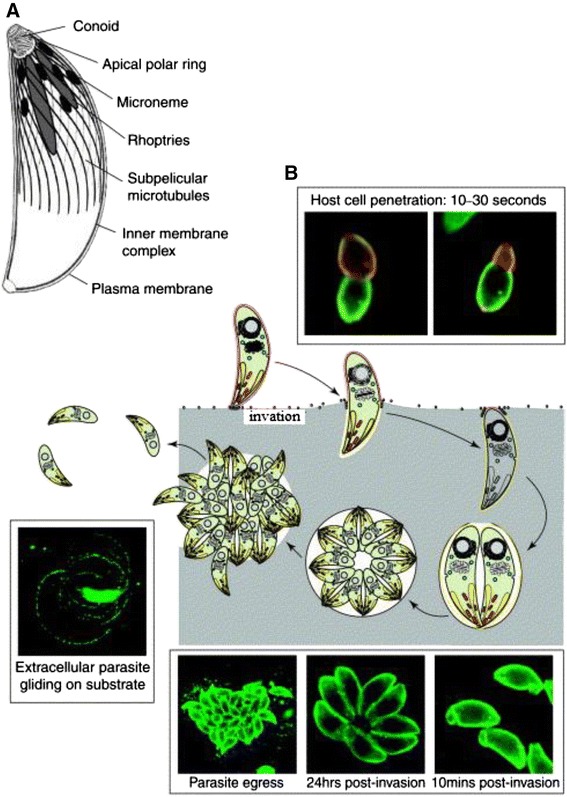
Host cell invasion by T. gondii. Reprinted from [11], Copyright © 2004, with permission from Elsevier. a Schematic representation of T. gondii tachyzoite and the subcellular structures involved in gliding motility and host cell invasion. b Cycle of host cell invasion and egress by T. gondii. This multi-step process includes the attachment to host cells, the discharge by the micronemes (red), the discharge by the rhoptries (yellow), the formation and sealing of the parasitophorous vacuole, intracellular parasite replication, lysis of the PVM and parasite egress [11]
