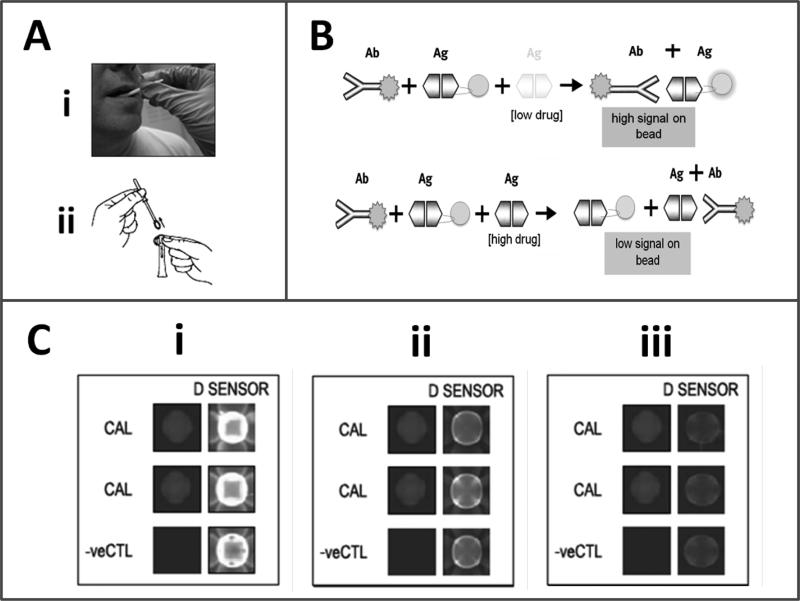
Figure 1.
Programmable BNC/oral fluid-based drug tests. Oral fluid sample collected by a swab (Ai) is extracted in assay buffer (Aii) and then delivered to the microfluidic cell hosting bead sensors arrayed on a microchip. In (B) shown are the schematic decoding the immuno-components of this competitive assay approach. In (C) shown are charge-coupled device (CCD)-captured images of a concentration-dependent response for the competitive-type p-BNC-based amphetamine test (i- control 0, ii- 10 and iii- 100 ng/mL amphetamine. Noted are a) the decrease in signal acquired on the drug sensors (D sensor) in response to the drug, b) the absence of signal on negative control beads (-ve CTL) and c) the consistency in signal intensity on the calibrator beads upon completion of three independent assay runs.