Figure 6. Schematic model of the proposed roles of a 4-CRD galectin in the uptake of microalgae, bacteria, and protozoan parasites by hemocytes of an aquatic mollusk.
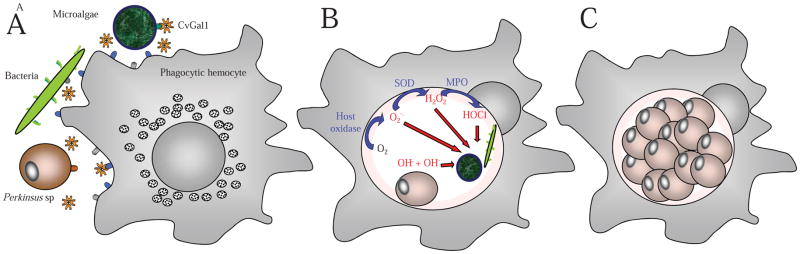
(A) The 4-CRD galectin CvGal1 from the eastern oyster (C. virginica) is secreted by the hemocytes and can cross-link the blood group oligosaccharide moieties on the hemocyte surface to glycans of similar topology on the surface of microalgae (Tetraselmis sp), bacteria, and the parasite P. marinus. (B) CvGal1-mediated recognition and cross-linking promotes phagocytosis by opsonic effect, and the microalgae and bacteria are killed in the hemocyte phagosome by reactive oxygen species produced during the respiratory burst. P. marinus escapes oxidative stress by expression of anti-oxidative enzymes (Superoxide dismutases, ascorbate-dependent peroxidases, etc). (C) P. marinus survives intracellular killing and proliferates within the hemocyte, eventually causing systemic infection and death of the oyster host.
