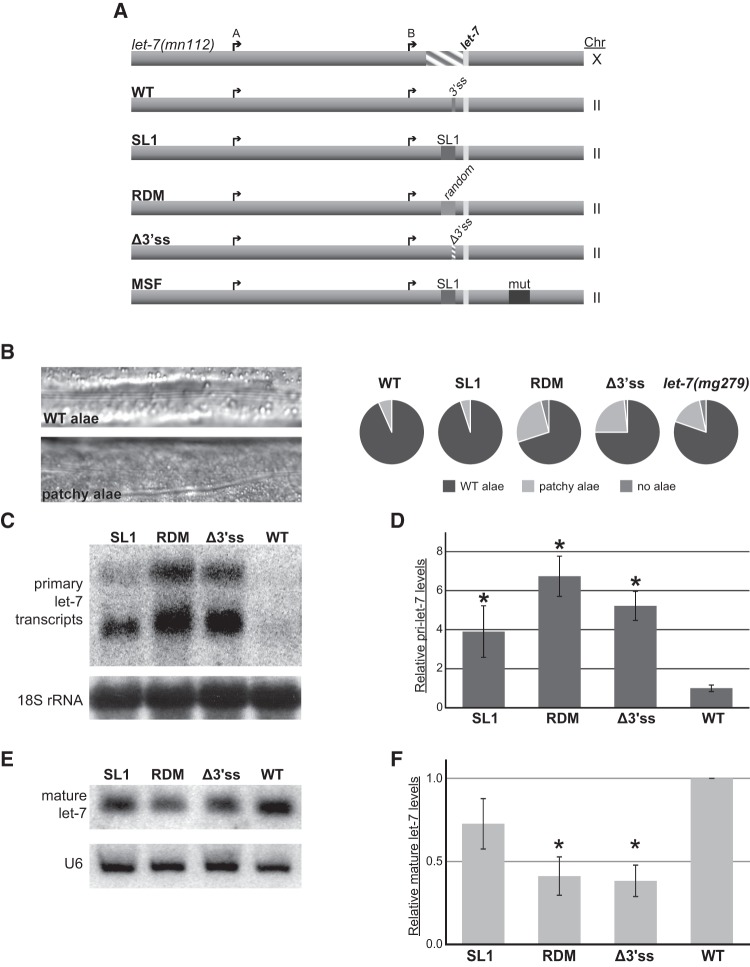
FIGURE 2.
Splicing is important for let-7 biogenesis in vivo. (A) Single copy transgenes with altered versions of the trans-splice site were inserted in Chromosome (Chr) II and expressed in the let-7(Δmn112) (Chr X) null mutant background to test for effects on rescue activity and let-7 biogenesis. The arrows represent let-7 A and B transcriptional start sites, the striped area represents the mn112 deletion, and the light rectangle is indicative of the mature let-7 sequence. In addition to the wild-type (WT) rescue construct, which contains the let-7 promoter regions, transcriptional start sites, and the 3′ splice site (3′ss) recognized by the spliceosome, four mutated versions of the let-7 transgene were generated. The “pre-spliced” construct (SL1) replaces the 3′ ss with the 22-nt splice-leader sequence. The “random” construct (RDM) replaces the 3′ ss with a 22-nt sequence that is similar in GC content to the SL1 sequence but is predicted to support a different secondary structure. The splice site knockout (Δ3′ss) is missing 7 nt essential for splicing recognition. The “misfolded” construct (MSF) contains the SL1 sequence in place of the 3′ ss but also includes a 48-nt mutation that creates a hairpin at the base of the pre-let-7 hairpin, similar to the unspliced secondary structure. (B) Analysis of the alae formation phenotype. Alae are a group of three cuticular ridges that form along the length of the adult C. elegans worm. Examples of alae in WT and worms that have insufficient let-7 activity, which results in “patchy” and gapped alae, are shown. Alae were analyzed by high-powered microscopy in transgenic worms and in a mutant that expresses twofold reduced levels of mature let-7 (let-7(mg279)). Results for RDM are presented as the average of two independent experiments where n = 25, while all other strains are presented as the average of three independent experiments where n = 20 in each. (C–F) Total RNA from triplicate L4 staged SL1, RDM, Δ3′ss, and WT transgenic worms was used for Northern blot and qRT-PCR analyses. Worms with the MSF transgene were inviable and, thus, could not be analyzed for let-7 expression. (C) Representative agarose Northern blot of primary let-7 expression. Detection of 18S ribosomal RNA serves as a loading control. (D) Quantitative RT-PCR of transgenic worms where pri-let-7 (all isoforms) levels were normalized to 18S rRNA and relative expression is compared with average WT expression. Standard error is depicted. (*) P < 0.05. (E) Representative PAGE Northern blot of mature let-7 expression. U6 snRNA serves as a loading control. (F) TaqMan qRT-PCR of mature let-7 normalized to 18S rRNA levels relative to WT. Standard error is depicted. (*) P < 0.05.