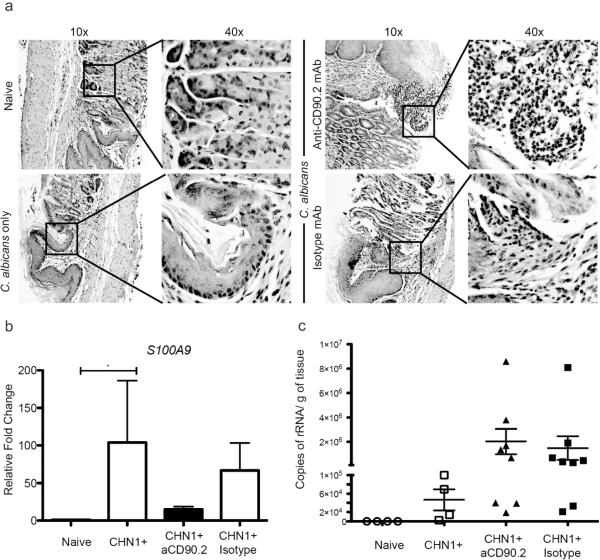
Figure 8.
C. albicans infection of the gastric mucosa is resistant to ILC dependent increases in calprotectin. Groups of rag1−/− mice were infected with C. albicans and treated with ILC-depleting antibody (anti-CD90.2) or an isotype matched control antibody (n ≥ 8). (a) Representative H&E stained stomach sections demonstrating the primary location and nature of lesions in response to infection. (b) Calprotectin subunit S100A9 levels were determined by semi-quantitative PCR on total RNA isolated from the gastric mucosa (± SEM). (c) Fungal load was determined by quantitative PCR of the ITS region of the rRNA gene of C. albicans and reported as copy number per gram of stomach tissue (± SEM). * P<0.05.