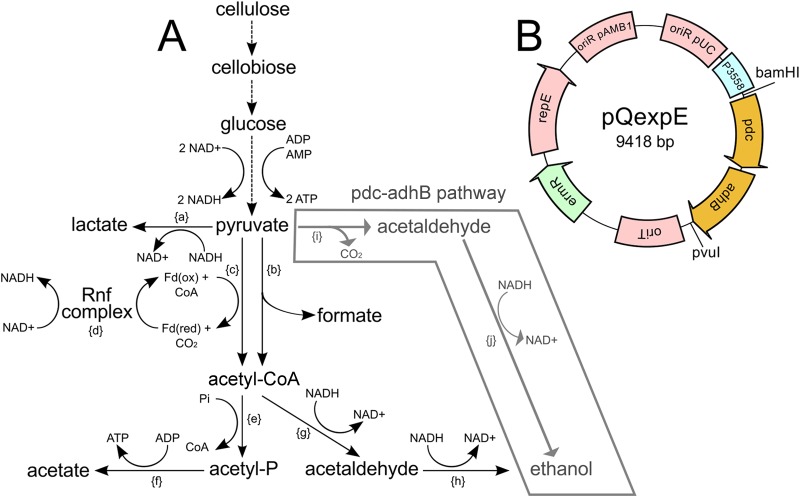
FIG 4.
(A) Diagram of C. phytofermentans carbon metabolism showing insertion of the Z. mobilis pdc-adhB alternative ethanol formation pathway. Enzymatic steps: {a}, lactate dehydrogenase (Cphy1117); {b}, pyruvate formate lyase (Cphy1174); {c}, pyruvate ferredoxin oxidoreductase (Cphy3558); {d}, Rnf ferredoxin:NAD+ oxidoreductase complex (Cphy0211 to Cphy0216); {e}, phosphate acetyltransferase (Cphy1326); {f}, acetate kinase (Cphy1327); {g}, acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (Cphy1428 or Cphy3925); {h}, alcohol dehydrogenase (Cphy3925 or Cphy1029); {i}, Zymomonas mobilis pyruvate decarboxylase (pdc); {j}, alcohol dehydrogenase (adhB). Dashed lines represent multienzyme reactions where all enzymes are not listed. (B) Plasmid map of pQexpE for pdc-adhB expression in C. phytofermentans. Plasmid features: Gram-negative pUC origin of replication (oriR pUC), C. phytofermentans pyruvate ferredoxin oxidoreductase promoter (P3558) to express the Z. mobilis pdc-adhB genes, the RP4 conjugal origin of transfer (oriT), the Gram-negative/Gram-positive erythromycin resistance gene from TN1545 (ermR), the Gram-positive pAMB1 origin (oriR pAMB1), and repE-encoded protein.