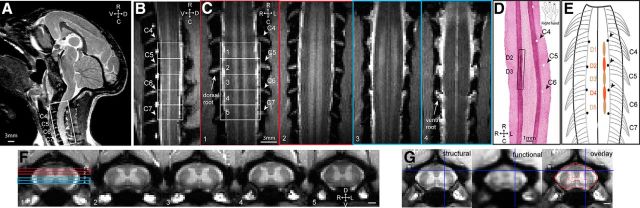
Figure 1.
Experimental set up for fMRI of the cervical spinal cord in anesthetized monkeys at 9.4 T. A, T2-weighted middle sagittal MRI image (taken from a different imaging session with a volume coil) shows visualization of cervical spinal afferent bundles (white stripes) and the imaging field of view (white outline box) over the cervical spinal cord. D, Dorsal; V, ventral; R, rostral; C, caudal. B, Sagittal view of the spinal cord on a MTC image. Ventral roots are apparent as white bundle strips (labeled as C4–C7). Five white rectangular outlines show the placements of five axial images. C, Four coronal images taken through the dorsal (two red outlined images) and ventral (two light blue outliend images) parts of the spinal cord across both DHs and VHs. Placements of the four coronal images over the DHs and VHs are shown on the first axial image in F. GM of spinal horns appeared as two vertical higher intensity white strips on coronal images. The superintense white strips on outer layers of the spinal cord represent space filled with CSF. Cervical dorsal and ventral nerve roots (C4–C7) are visible as horizontal hyperintensity stripes residing between signal void (s) and highlighted by white arrows. D, Aligned coronal section of spinal cord tissue stained with CTB. The rectangular black line box indicates the location of CTB terminal labeling resulting from tracer injections into distal pads of digits 2 and 3. White pinholes on the opposite side represent landmarks made on the centers of C5–C7 dorsal afferents entry zones on the surface of the spinal cord. R, Right; L, left; R, rostral; C, caudal. The schematic hand insert shows the injection sites of CTB tracer on the distal finger pads of digits 2 and 3 of a right hand. E, Schematic illustration shows the spatial relationships between the dorsal nerve roots and the digit afferent terminals determined by tracer injections (for original data, see Florence et al., 1991; Qi et al., 2011). Black dots indicate the pinholes locations. F, One set of five representative anatomical axial MTC images. Unlabeled scale bars, 1 mm. R, Right; L, left; D, dorsal; V, ventral. Slices 1–5, Rostral to caudal. G, Aligned MTC anatomical (top), fMRI (middle), and the overlap (bottom) images. Red outlines in the overlap image represent the fMRI boundaries of butterfly-shaped GM and spinal cord. Blue lines indicate a corresponding alignment landmark.