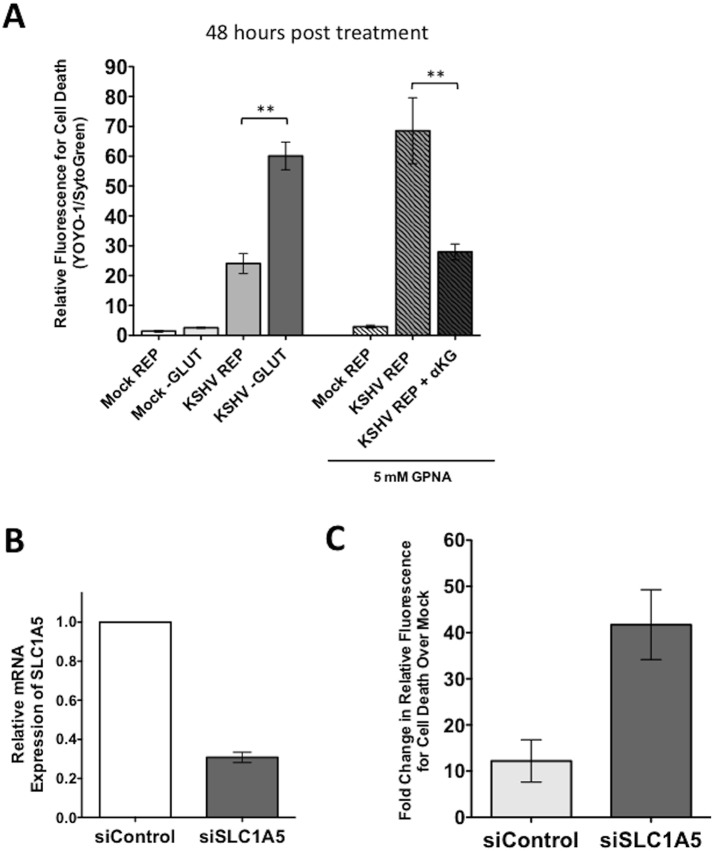
Fig 6. Endothelial cells latently infected with KSHV require the glutamine transporter SLC1A5 for survival.
(A) 20 hpi, Mock- or KSHV-infected TIME cells were re-seeded into 24-well plates in triplicate. Cells were treated with replete (REP) media in the presence or absence of 5mM GPNA, a specific inhibitor of SLC1A5, in the presence or absence of 3.5 mM αKG and scanned on the Typhoon at 48 hours post treatment (72 hpi). Glutamine-deprived (-GLUT) controls were included for comparison. Data shown is the average relative fluorescence (YOYO-1 positive cells/SytoGreen24 positive cells) from three independent experiments. Error bars represent the SEM. A p-value < 0.01 is denoted by two asterisks. (B) TIME cells were transfected with siControl or siSLC1A5. siSLC1A5 treatment leads to an approximately 70% reduction in SLC1A5 expression, determined by qRT-PCR for SLC1A5. Expression was normalized to the housekeeping gene GAPDH. (C) Twenty-four hours post transfection of TIME cells with siControl or siSLC1A5, cells were Mock- or KSHV-infected. Upon completion of the infection, cells were treated with replete media containing YOYO-1 to identify dead cells or SytoGreen24 to identify total cell number. 48 hpi (72 hours post transfection), cells were scanned on the Typhoon. Data shown is the average fold change in relative fluorescence of KSHV over mock cells (YOYO-1 positive cells/SytoGreen24 positive cells) from two independent experiments. Error bars represent the SEM.