Fig 8. Schematic of glutamine metabolism via glutaminolysis during KSHV infection of endothelial cells.
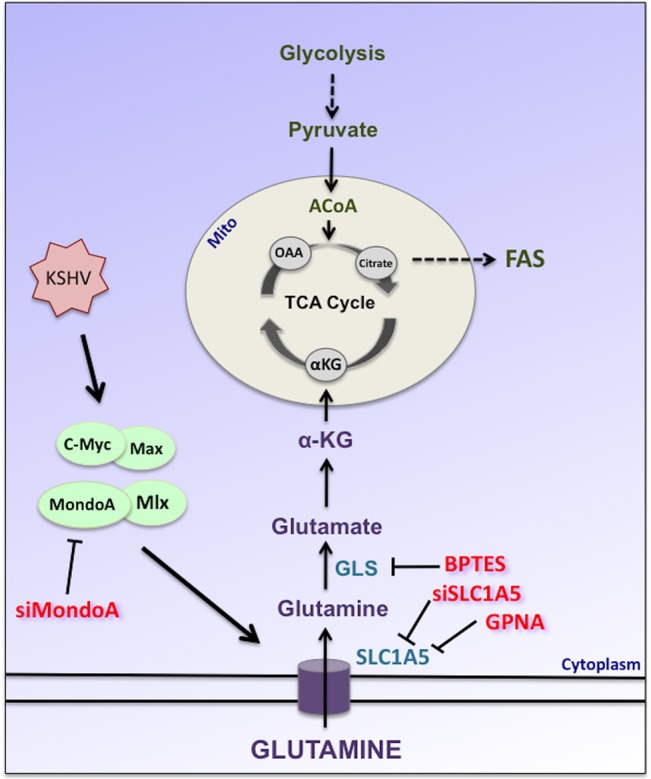
Latent KSHV infection induces and requires the Myc/Max and MondoA/Mlx heterodimers leading to the induction of the glutamine transporter SLC1A5 during latent KSHV infection. Upon entering the cell, glutamine is deaminated twice to form αKG. αKG can enter the TCA cycle where it can be utilized to support bioenergetics and the metabolism of biosynthetic precursors. GPNA or siSLC1A5 treatment was used to specifically inhibit glutamine transport via SLC1A5. BPTES is a specific inhibitor of glutaminase (GLS), the first enzyme of glutaminolysis. siMondoA treatment was used to specifically inhibit MondoA-mediated activation of glutaminolysis.
