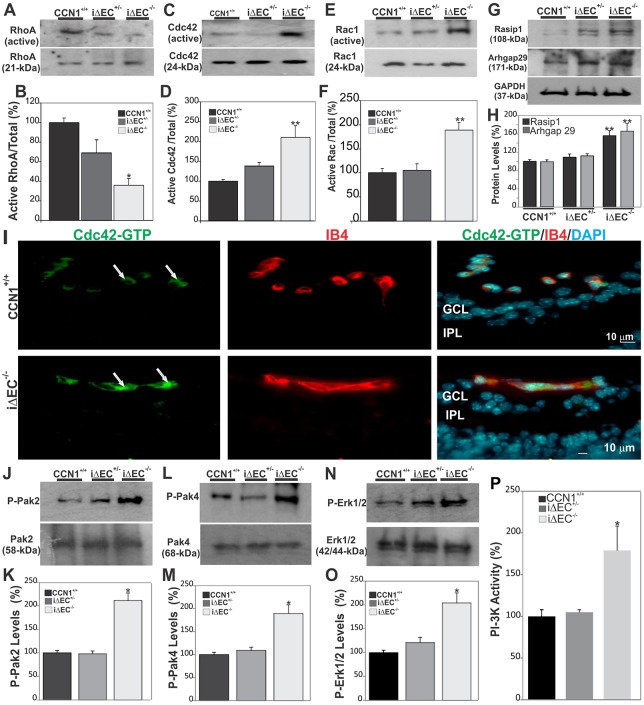
Fig. 6.
Loss of CCN1 potentiates VEGF-R2 downstream signaling through Rho GTAse and MAPK activation during retinal vessel formation. (A-F) Rho A, Cdc42 and Rac activation status as determined by GTPase assay in retinal extracts from wild-type, iΔEC+/− and iΔEC−/− mice. Protein band signals were normalized to total input of each GTPase (B,D,F). **P<0.01 versus CCN1+/+ (n=3). (G,H) Expression of signaling kinases (Rasip1 and Arhgap29) upstream of Cdc42/Rac1 GTPases. The same blots were stripped and washed before subsequent incubation with antibody against the indicated proteins. Experiments were performed on at least three different retinal lysate preparations with similar results. **P<0.05 versus CCN1+/+. (I) Effects of CCN1 deletion on the activation of Cdc42. Transverse sections of P6 retinas were labeled with either Cdc42-GTP-specific antibody or IB4. Note that the active Cdc42-GTP was largely localized within the vasculature of both control CCN1+/+ and iΔEC−/− mice (arrows). GCL, ganglion cell layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer. (J-O) Phosphorylation status of signaling kinases (Pak2, Pak4 and Erk1/2) downstream of Cdc42/Rac1 GTPases. Phosphorylated protein levels were normalized to those of the corresponding non-phosphorylated protein signal. *P<0.01 versus CCN1+/+. (P) PI3-K activity in retinal protein lysates as determined by PI3-K activity ELISA assay. *P<0.001 versus CCN1+/+ (n=4).