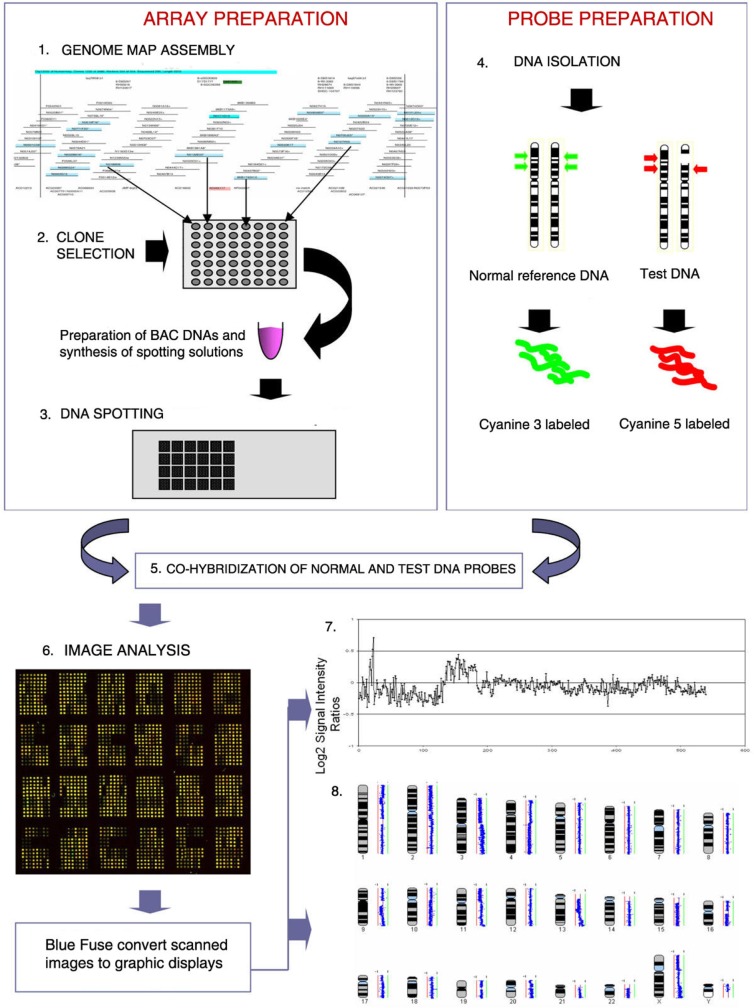
Figure 1.
This figure shows the steps in BAC array CGH. (1) BAC clones are selected from a physical map of the genome. (2) DNA samples are extracted from selected BAC clones and their identity is confirmed by DNA fingerprinting or sequence analysis. (3) A multi-step amplification process generates sufficient material from each clone for array spotting. Each clone is spotted in replicate onto a solid support. (4) Reference DNA and test DNA are differentially labeled with cyanine 3 and cyanine 5 respectively. (5) The two labeled products are combined and hybridized onto the spotted slide. (6) Images from hybridized slides are obtained by scanning in two channels. Signal intensity ratios from individual spots can be displayed as a simple plot (7) or by using more complex software such as SeeGH, which can display copy number alterations throughout the whole genome (8).