Figure 2.
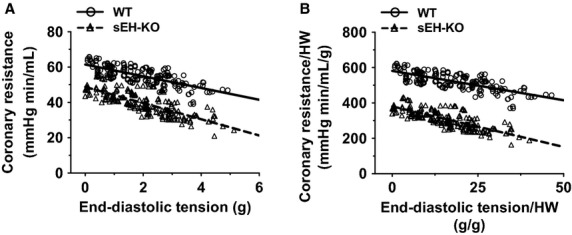
The correlation between coronary vascular resistance and end-diastolic tension in isolated hearts of WT (n = 12) and sEH-KO (n = 9) mice. (A) Correlation coefficient is −0.7316 (P < 0.0001) and −0.7702 (P < 0.0001) in WT and sEH-KO hearts, respectively. The slope of regression line is -3.329 ± 0.2358 (WT) and −4.582 ± 0.271 (sEH-KO). The difference between the two slopes is statistically significant (P < 0.001). (B) Changes in end-diastolic tension and coronary resistance were normalized by heart weights. Correlation coefficient is −0.7348 (P < 0.0001) and −0.7715 (P < 0.0001) in WT and sEH-KO hearts, respectively. The slope of regression line is −3.322 ± 0.2346 (WT) and −4.593 ± 0.2722 (sEH-KO). The difference between the two slopes is statistically significant (P < 0.0001).
