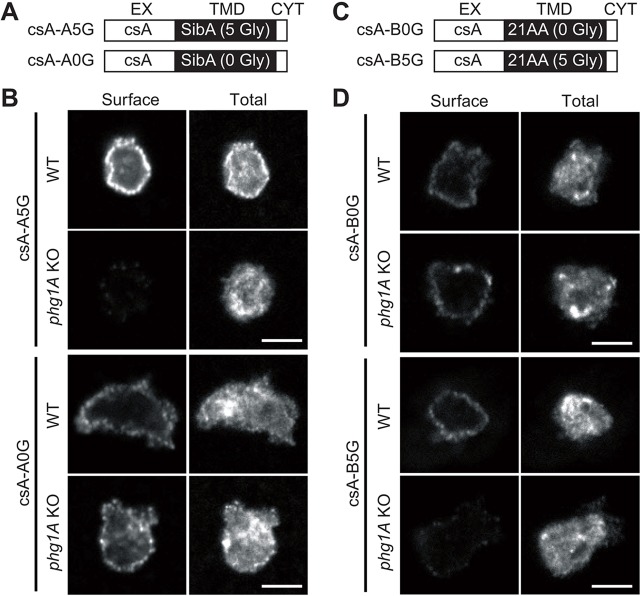
Fig. 1.
Phg1A ensures efficient cell surface localization of proteins harboring the SibA glycine-rich TMD. All pictures were taken with the same confocal microscope (Zeiss LSM700) and the same setting allowing direct comparison. Scale bar: 5 µm. (A) The csA-A fusion proteins are composed of the extracellular domain of csA, the glycine-rich TMD of SibA (csA-A5G) or a mutated form without glycine residues (csA-A0G), and a short cytoplasmic tail (see Table 1). (B) Fusion proteins were labeled before (Surface) and after (Total) permeabilization by immunofluorescence in WT or phg1A KO cells, using an antibody specific for the csA extracellular domain. (C) CsA-B fusion proteins are composed of the extracellular domain of csA, a hydrophobic TMD without glycine residues (csA-B0G) or a mutated form with five glycine residues added (csA-B5G), followed by a short cytoplasmic tail (see also Table 1). (D) Fusion proteins were expressed in Dictyostelium WT or phg1A KO cells and labeled before (Surface) and after (Total) permeabilization by immunofluorescence.