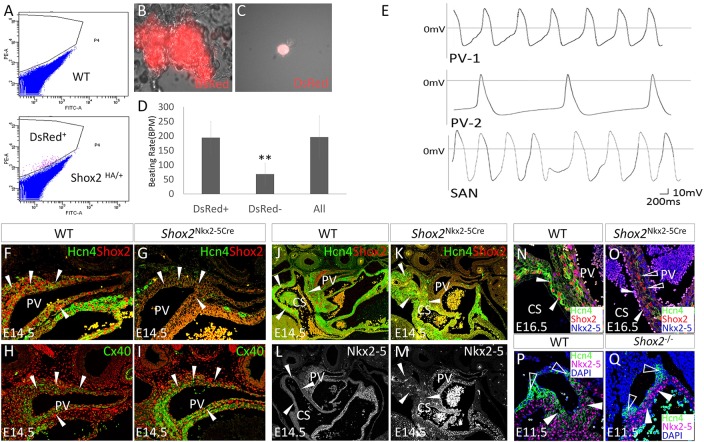
Fig. 4.
Shox2 potentiates a pacemaker-like phenotype in the PV myocardium. (A) Separation of Shox2+ cells from the surrounding Shox2− cells of the PV myocardium of E14.5 Shox2HA embryo by FACS. (B) A representative beating clump composed of Shox2+ cells. (C) An isolated DsRed+ cell from E14.5 Shox2HA PV myocardium used for whole-cell patch recording. (D) Comparison of beating rate of cell clumps consisting of Shox2+, or Shox2−, or mixed cells isolated from the PV of E14.5 Shox2HA mice (n=5). **P<0.01. (E) Two representative configurations (PV-1 and PV-2; n=3 each) in Shox2+ cells from the E14.5 PV myocardium, as compared with that seen in SAN cells isolated from an embryo of the same stage. (F-I) Immunohistochemistry shows reduced Hcn4 and enhanced Cx40 levels (arrowheads) in the PV myocardium of E14.5 Nkx2-5IRESCre/+;Shox2F/F (Shox2Nkx2-5Cre) mice (G,I), as compared with controls (F,H). (J-M) Immunohistochemistry shows complementary patterns of Hcn4 and Nkx2-5, despite the lack of Shox2, in the coronary sinus (arrowheads) of E14.5 Shox2Nkx2-5Cre mice (K,M), as compared with controls (J,L; note that panel J is the same as Fig. 1B). (N,O) Hcn4 is ablated in the coronary sinus myocardial cells (arrowheads) at E16.5 when Nkx2-5 protein accumulation becomes prominent in Shox2Nkx2-5Cre mice (O) compared with controls (N). Open arrowheads point to cells that escape Shox2 deletion and express Hcn4. (P,Q) Hcn4 expression is sustained in Nkx2-5− SAN head (open arrowheads) but ablated from the Nkx2-5+ SAN junction (arrowheads) of E11.5 Shox2−/− mice (Q), as compared with the control (P). CS, coronary sinus; PV, pulmonary vein.