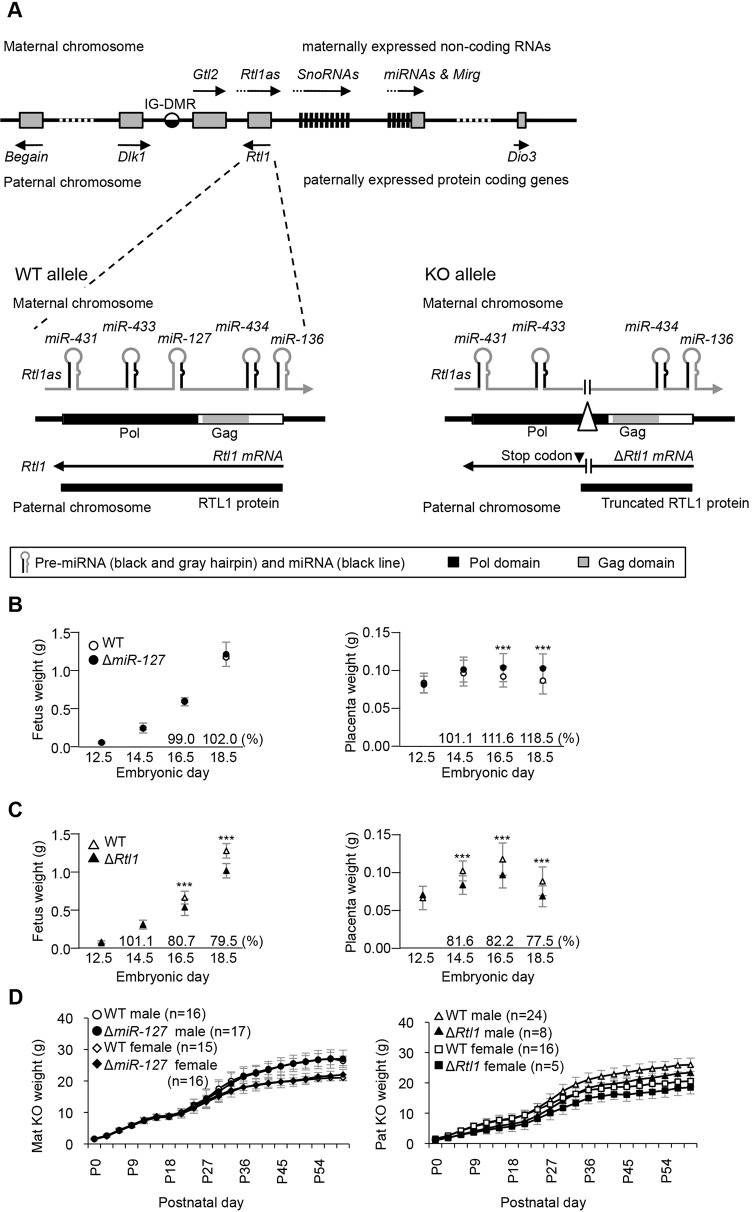
Fig. 1.
Structure of the Rtl1 locus and pre- and postnatal growth of miR-127 and Rtl1 knockout mice. (A) Schematic presentation of the mouse Dlk1-Dio3 cluster. (Lower left) The WT Rtl1 locus (exon 3). Rtl1 is expressed from the paternal chromosome and Rtl1as is exclusively transcribed from the maternal chromosome. (Lower right) The knockout (KO) allele. The paternally transmitted deletion introduces an in-frame stop codon that results in premature termination of RTL1. The maternally transmitted deletion lacks miR-127 expression. (B,C) Prenatal growth of ΔmiR-127 mice and ΔRtl1 mice, respectively. Left and right panels show embryonic and placental growth curves in mutant and WT littermates from E12.5 to E18.5. All embryos and placentas were collected from the N6 and N7 generation. (D) Postnatal growth curve of ΔmiR-127 (left) and ΔRtl1 (right) from birth to 2 months. Weights were measured every 3 days. ΔRtl1 mice were significantly smaller than WT. ***P<0.005 (Student's t-test). Error bars indicate s.d.