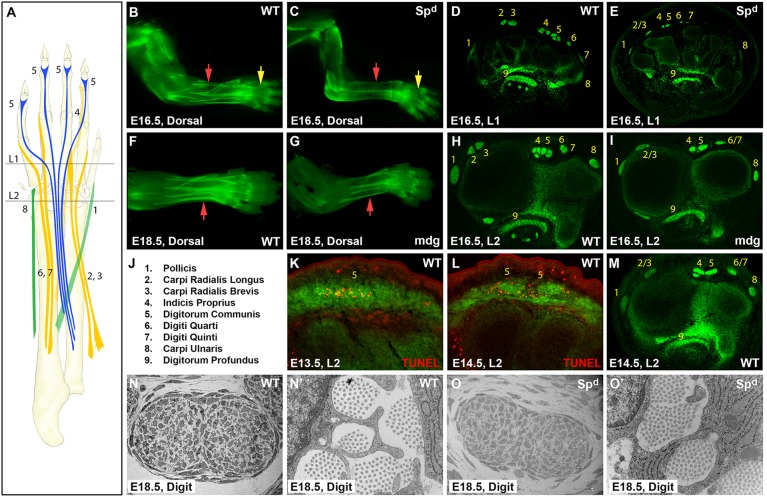
Fig. 1.
Developmental modularity of limb tendons is revealed by muscle-independent autopod tendon development and muscle-dependent zeugopod tendon development. (A) Schematic of long extensor tendons from their muscle origins to skeletal insertions. Levels of transverse section are indicated (L1, L2). (B,C) Whole-mount and (D,E) transverse section images of ScxGFP WT and Spd mouse limbs at E16.5. (F,G) Whole-mount and (H,I) transverse sections of WT and mdg limbs at E16.5 and E18.5. (J) Numerical tendon assignments. (K,L) TUNEL staining of WT EDC tendon near the carpals at E13.5 and E14.5. (M) ScxGFP WT limb at E14.5. (N-O′) TEM of WT and Spd FDP tendon at digit level. Yellow and red arrows highlight autopod and zeugopod tendons, respectively.