Figure 5.
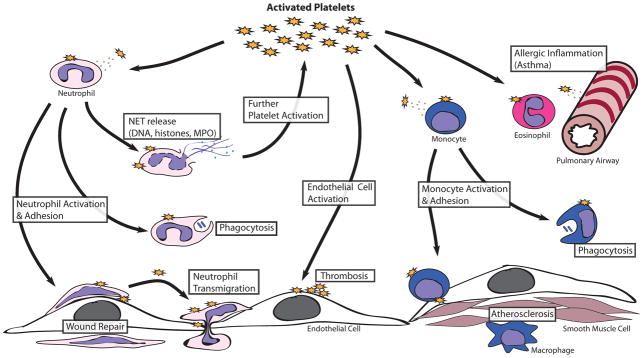
Selected examples of pro-inflammatory effects of platelets resulting in functional consequences on leukocytes. Platelets interact with leukocytes through both adhesive mechanisms as well as release of cytokines/chemokines. This results in leukocyte activation and enhanced leukocyte-endothelial adhesion. Through these mechanisms, platelets participate in several normal and pathologic immune functions including microbial killing, leukocyte homing, wound healing, allergic inflammation, and atherosclerosis, among others.
