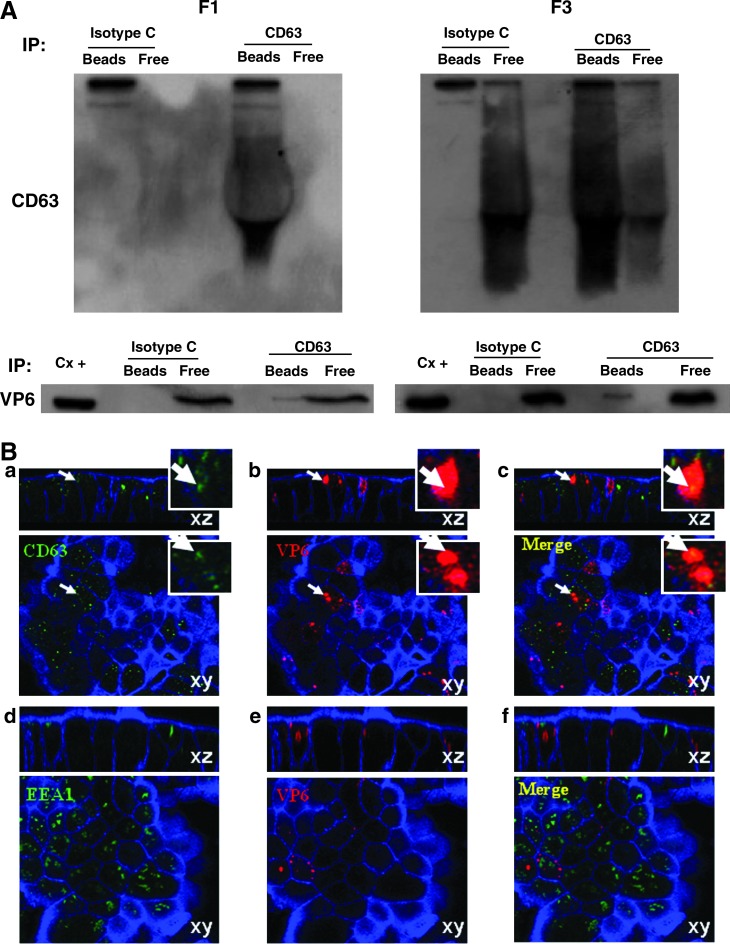
FIG. 2.
RV VP6 is associated with vesicles that express CD63 in vitro. (A) At 24 hpi F1 and F3 from RRV-infected Caco-2 cells were subject to IP with magnetic beads coupled to anti-CD63 or an isotype control mAb. Proteins captured by the beads (Beads), or remaining in the supernatant (Free), were detected by WB using mAbs anti-CD63 and anti-VP6 (mouse mAb 1026). Representative WBs detecting CD63 and VP6 of two independent experiments performed with F1, and six using F3 with similar results, are shown. (B) Confocal microscopy of infected Caco-2 cells at 16 hpi with some co-localization of VP6 (mAb 1E11), and CD63 (a CD63 [green], b VP6 [red], and c merge), but no co-localization of VP6 with the EEA1 (green), used as a control (d EEA-1, e VP6, and f merge). Blue staining corresponds to actin. The white arrows illustrate a co-localization example that is enlarged in the upper right images. Each panel is composed of an xz section (top), and an xy section (bottom).