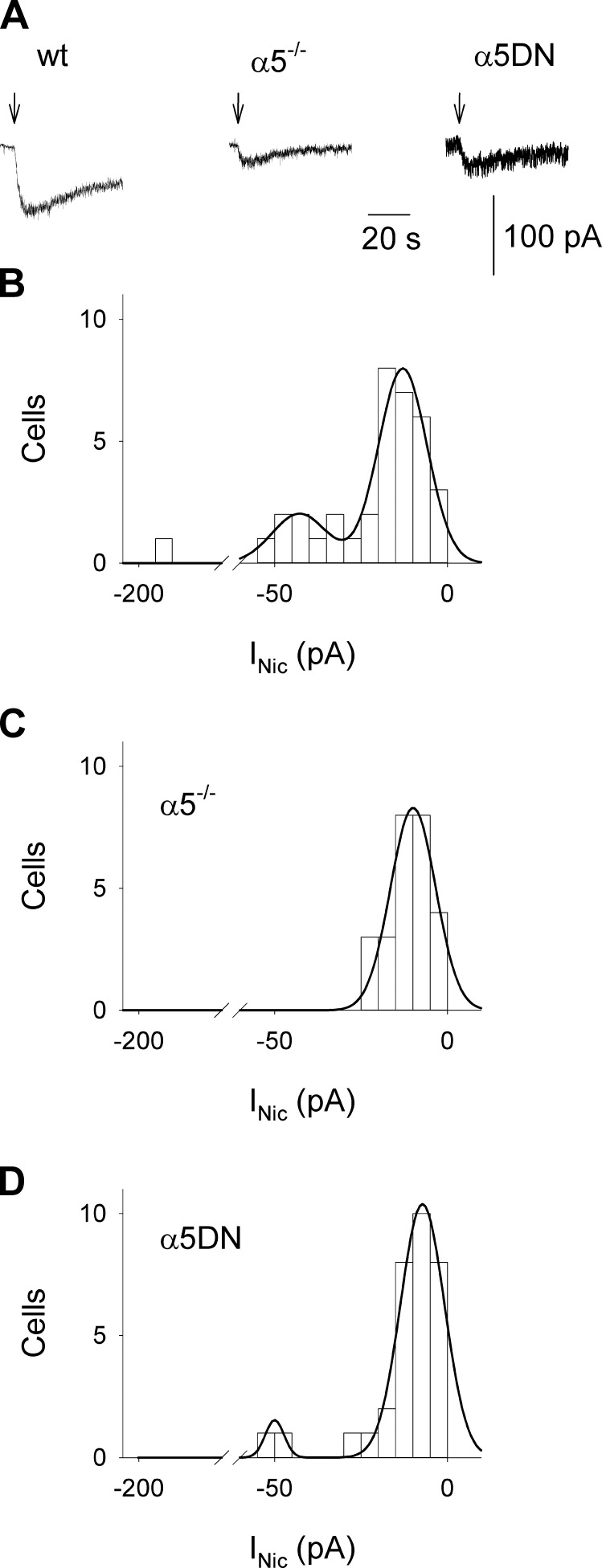
Figure 2.
α5 Subunit is essential for the presence of a high-amplitude subpopulation of inward currents mediated by heteromeric nAChRs in neurons in mouse VTA slices, with α5DN less efficient than WT subunit. A) Typical nicotine-evoked inward currents (INic) recorded in the presence of 10 nM MLA, 20 μM CNQX, 20 μM AP5, and 10 μM bicuculline in VTA neurons from WT, α5−/−, and α5DN mice, as indicated. Arrows indicate nicotine pressure applications (100 μM for 2 seconds). B) Histogram representing the current amplitude distribution for WT neurons (n = 36). Data were best fitted to the sum of 2 Gaussian functions, with mean ± SD values of −13 ± 7 and −43 ± 8 pA, respectively. C) Histogram representing the current amplitude distribution for α5−/− neurons (n = 26). Data were best fitted to a single Gaussian function. Mean ± sd values were −10 ± 7 pA. D) Histogram representing the current amplitude distribution for α5DN neurons (n = 32). Data were best fitted to the sum of 2 Gaussian functions, with mean ± sd values of −7 ± 6 and −50 ± 3 pA, respectively.