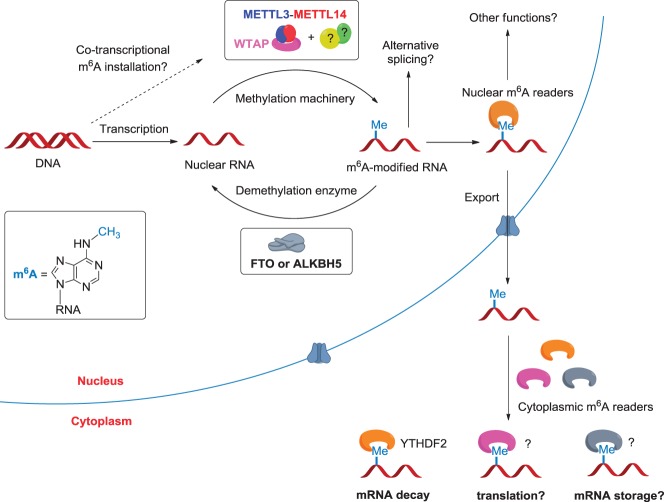
Figure 1.
Illustration of the cellular pathways of m6A in nuclear RNAs. The m6A methyltransferases and demethylases dynamically control the m6A methylation landscape within the nucleus. The m6A reader proteins preferentially bind to the methylated RNA and mediate specific functions. In the nucleus, m6A may affect alternative splicing of pre-mRNA and mature mRNA storage and export. After mature RNAs are exported to the cytoplasm, cytoplasmic m6A reader YTHDF2 can bind to the m6A-containing mRNAs to mediate mRNA decay. Other cytoplasmic readers could modulate mRNA translation and storage.