Figure 3.
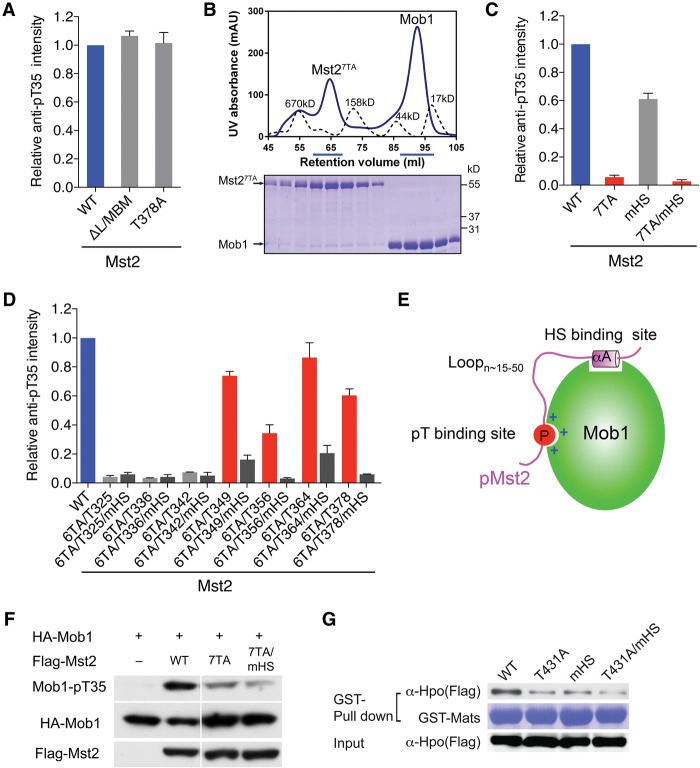
The Mst2 linker contains multiple pTM motifs for Mob1 binding. (A) Quantification of the relative Mob1-pT35 signals in kinase reactions containing the indicated Mst2 proteins. Means with range for two independent experiments are plotted. (B) UV traces of molecular weight standards (dashed line) and Mst27TA and Mob1 mixed at a 1:2 molar ratio (solid line) fractionated on a Superdex 200 gel filtration column. The underlined fractions were separated on SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie. (C) Quantification of the relative Mob1-pT35 signals in kinase reactions containing the indicated Mst2 proteins. Means with range for two independent experiments are plotted. (D) Quantification of the relative Mob1-pT35 signals in kinase reactions containing the indicated Mst2 proteins. Means with range for two independent experiments are plotted. (E) Schematic drawing of the bipartite Mob1–pMst2 interaction, which involves the binding of pTM and HS motifs connected by a flexible loop with variable length. (F) Immunoblots of lysates of HEK293 cells transfected with the indicated plasmids. (G). Immunoblots (top and bottom panels) of lysates of Drosophila S2R+ cells transfected with the indicated Flag-Hpo plasmids (Input) and proteins bound to GST-Mats beads. The GST-Mats protein bound to beads was stained with Coomassie (middle panel).